How Vector Clocks Ensure Ordering In Distributed Systems

Vector Clocks In Distributed Systems Geeksforgeeks Pdf In distributed systems, data consistency is a significant challenge. imagine a scenario where multiple users are editing a shared document simultaneously. when two users make changes at the. In this video, we explore **vector clocks**—a powerful tool to track event ordering and causality in distributed environments. learn how vector clocks detect conflicts, manage.

Logical Clocks In Distributed Systems Pdf Message Passing Understand vector clocks in distributed systems: how they track causality, maintain event ordering, and resolve conflicts. learn their structure, use cases, pros, limitations, and key variations. Vector clocks in distributed systems are a mechanism used to capture causality and the ordering of events in distributed systems. each node maintains a vector of clocks, where each entry represents its logical clock and that of other nodes. Discover the role of vector clocks in ensuring data consistency and integrity in distributed systems, and learn how to implement them effectively. Learn what a vector clock in distributed systems is and how this logical clock orders events without a global clock, with real examples and interview tips.

How Vector Clocks Ensure Ordering In Distributed Systems By Roopa Discover the role of vector clocks in ensuring data consistency and integrity in distributed systems, and learn how to implement them effectively. Learn what a vector clock in distributed systems is and how this logical clock orders events without a global clock, with real examples and interview tips. Logical clocks refer to implementing a protocol on all machines within your distributed system, so that the machines are able to maintain consistent ordering of events within some virtual timespan. One of the famous real life use case of vector clock is how dynamodb uses it to maintain ordering of events. dynamo is built to tolerate network partitions and it continues accepting writes even in case the nodes are unable to communicate across the partitions. Distributed algorithm to generate a snapshot of relevant system wide state (e.g. all memory, locks held, ) coordinator makes e.g. concurrent join leave easier what delivery orderings can we enforce? e.g. what if message m1 to p2 takes a loooong time? held back messages are delivered later as the result of the receipt of another message. Vector clocks are a logical time keeping mechanism that helps determine the partial ordering of events in a distributed system. unlike scalar clocks, which assign a single timestamp,.

Vector Clocks In Distributed Systems Geeksforgeeks Logical clocks refer to implementing a protocol on all machines within your distributed system, so that the machines are able to maintain consistent ordering of events within some virtual timespan. One of the famous real life use case of vector clock is how dynamodb uses it to maintain ordering of events. dynamo is built to tolerate network partitions and it continues accepting writes even in case the nodes are unable to communicate across the partitions. Distributed algorithm to generate a snapshot of relevant system wide state (e.g. all memory, locks held, ) coordinator makes e.g. concurrent join leave easier what delivery orderings can we enforce? e.g. what if message m1 to p2 takes a loooong time? held back messages are delivered later as the result of the receipt of another message. Vector clocks are a logical time keeping mechanism that helps determine the partial ordering of events in a distributed system. unlike scalar clocks, which assign a single timestamp,.
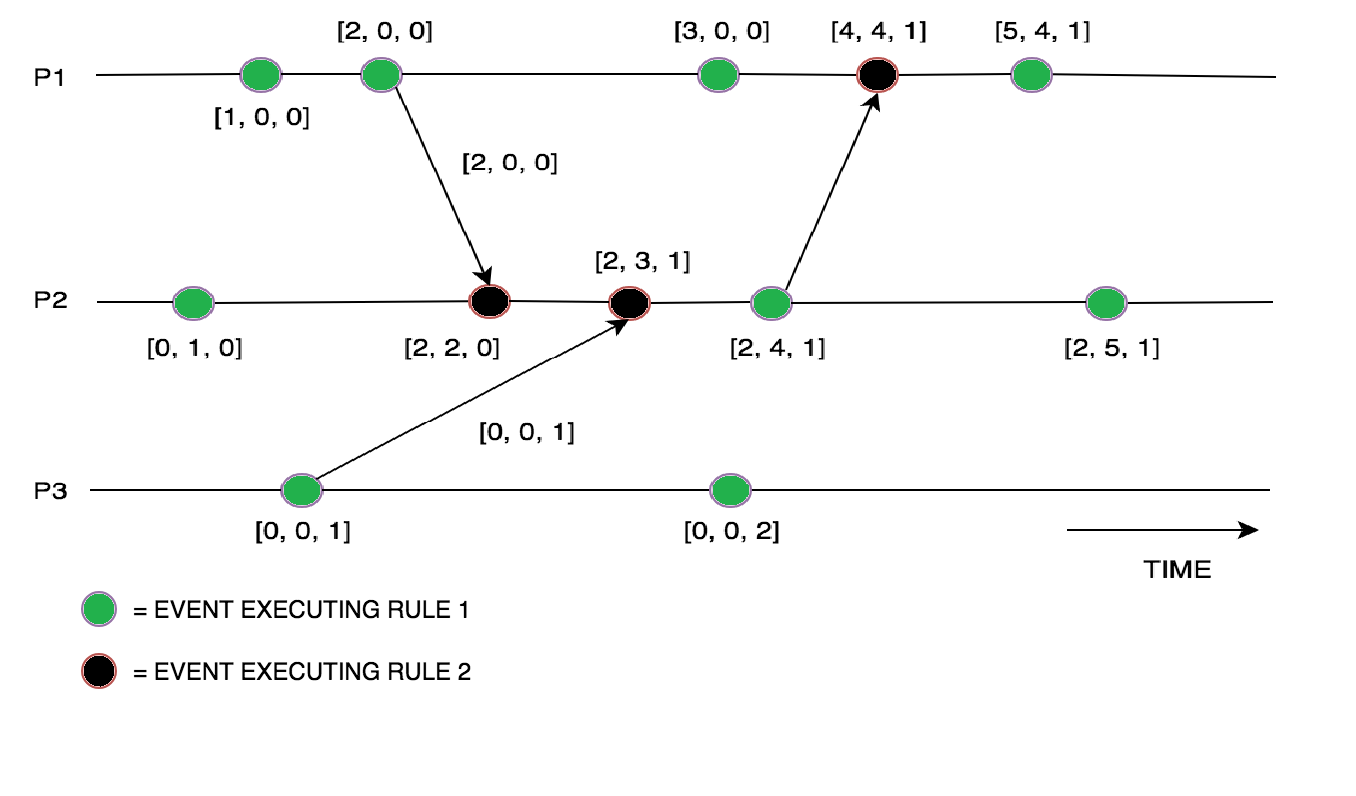
Vector Clocks In Distributed Systems Geeksforgeeks Distributed algorithm to generate a snapshot of relevant system wide state (e.g. all memory, locks held, ) coordinator makes e.g. concurrent join leave easier what delivery orderings can we enforce? e.g. what if message m1 to p2 takes a loooong time? held back messages are delivered later as the result of the receipt of another message. Vector clocks are a logical time keeping mechanism that helps determine the partial ordering of events in a distributed system. unlike scalar clocks, which assign a single timestamp,.
Comments are closed.