How To Use The Rank Eq Function In Excel
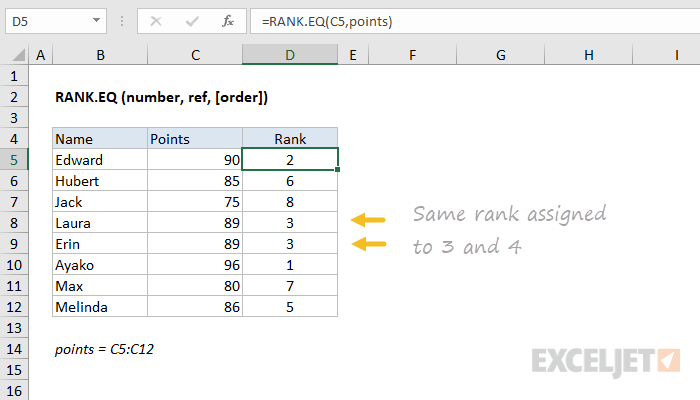
Excel Rank Eq Function Exceljet You can use the rank.eq function to calculate the rank of each value in a dataset. when values contain duplicates, rank.eq will assign the same rank to each tie value, and the subsequent rank will be skipped. Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers. its size is relative to other values in the list; if more than one value has the same rank, the top rank of that set of values is returned. if you were to sort the list, the rank of the number would be its position. rank.eq (number,ref, [order]).
Excel Rank Eq Function Exceljet How to use the excel rank.eq function the rank.eq function in excel ranks a number in a reference list of numbers. when two or more numbers clash, the top rank of that set is returned. syntax of rank.eq function =rank.eq (number,ref range, [order]). Whether you're organizing a sales leaderboard or sorting exam results, rank.eq is your go to function. in this article, we're diving deep into everything you need to know to master rank.eq. Learn how to use the rank.eq function in excel to identify the relative ranking of a value within a range of values. Rank.eq can work with non adjacent cell ranges by using named ranges or union references. this example uses a named range. the table assumes cells a2:b3 are named "annualsales". the rank.eq formula references this named range to rank q1 sales against all quarterly sales data.

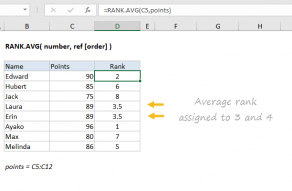
How To Use The Rank Eq Function In Excel Sheetaki Learn how to use the rank.eq function in excel to identify the relative ranking of a value within a range of values. Rank.eq can work with non adjacent cell ranges by using named ranges or union references. this example uses a named range. the table assumes cells a2:b3 are named "annualsales". the rank.eq formula references this named range to rank q1 sales against all quarterly sales data. Learn how to do ranking in excel based on multiple criteria using rank, countifs, sumproduct, and techniques for unique and grouped rankings. Excel added two improved versions of the rank () function in excel 2010: rank.eq () and rank.avg (). to handle the tie in the data, these two functions can be used. 1. rank.eq () – equal ranking. returns the rank of a number in the list of numbers same behaviour as rank (). Use with conditional formatting: rank.eq can be used with conditional formatting to highlight specific ranks or top bottom values. if number is not found in ref, excel returns a #n a error.ensure that ref contains at least one numeric value, or excel will return a #value! error. To rank in descending order, enter =rank.eq (b1, a1:a10, 0). to rank in ascending order, enter =rank.eq (b1, a1:a10, 1). make sure the range in the ref argument includes valid numerical values. the rank.eq function ranks numbers based on their order in the reference array or range.

How To Use The Rank Eq Function In Excel Sheetaki Learn how to do ranking in excel based on multiple criteria using rank, countifs, sumproduct, and techniques for unique and grouped rankings. Excel added two improved versions of the rank () function in excel 2010: rank.eq () and rank.avg (). to handle the tie in the data, these two functions can be used. 1. rank.eq () – equal ranking. returns the rank of a number in the list of numbers same behaviour as rank (). Use with conditional formatting: rank.eq can be used with conditional formatting to highlight specific ranks or top bottom values. if number is not found in ref, excel returns a #n a error.ensure that ref contains at least one numeric value, or excel will return a #value! error. To rank in descending order, enter =rank.eq (b1, a1:a10, 0). to rank in ascending order, enter =rank.eq (b1, a1:a10, 1). make sure the range in the ref argument includes valid numerical values. the rank.eq function ranks numbers based on their order in the reference array or range.

How To Use The Rank Eq Function In Excel Sheetaki Use with conditional formatting: rank.eq can be used with conditional formatting to highlight specific ranks or top bottom values. if number is not found in ref, excel returns a #n a error.ensure that ref contains at least one numeric value, or excel will return a #value! error. To rank in descending order, enter =rank.eq (b1, a1:a10, 0). to rank in ascending order, enter =rank.eq (b1, a1:a10, 1). make sure the range in the ref argument includes valid numerical values. the rank.eq function ranks numbers based on their order in the reference array or range.
Comments are closed.