How To Subtract Mixed Numbers Basic Math Review Of Fractions And Mixed Numbers

Subtracting Mixed Numbers From Whole Numbers Pdf Fraction Abstract background bleeding is a recognized complication of native percutaneous renal biopsy. this study aimed to describe the incidence of major bleeding after biopsy in a single centre over a 15 year period and examine factors associated with major bleeding. The kidney biopsy is a critical diagnostic and prognostic tool for evaluation of patients with kidney disease. 1 its results can guide management and provide information on response to treatment. 2 due to the high blood flow through the kidneys, which receive approximately 20% of the cardiac output, 3 the major risks of kidney biopsies are related to bleeding. bleeding complications can range.

Mash 5th 6th Class Fractions Subtracting Mixed Numbers These findings confirm that the overall risk of major bleeding following solid organ biopsy is low, with splenic and renal biopsies entailing the highest risk. delayed bleeding events are infrequent but should warrant consideration in guiding postprocedural follow up. Renal biopsy is an important procedure in determining renal disease etiology and prognosis, guiding its management and monitoring renal transplant function and viability.1 5 automated biopsy instruments and real time ultrasound guidance have improved safety6 since the procedure was first described in 1951,7 but there remains a risk of bleeding. The aim of this study was to investigate the incidence of hemorrhagic complication rates after native kidney biopsy performed with real time ultrasonographic guidance and automated spring loaded biopsy device through systematic review and meta analysis of the literature. The aim of our study was to evaluate the incidence of postbiopsy bleeding complications in a prospective cohort of patients who underwent real time ultrasound guided automated percutaneous renal biopsy of native kidney in a single nephrology center.
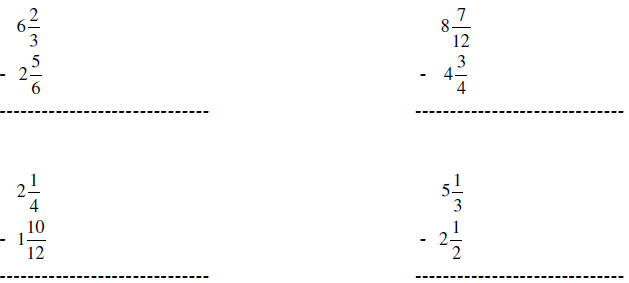
Subtracting Mixed Numbers The aim of this study was to investigate the incidence of hemorrhagic complication rates after native kidney biopsy performed with real time ultrasonographic guidance and automated spring loaded biopsy device through systematic review and meta analysis of the literature. The aim of our study was to evaluate the incidence of postbiopsy bleeding complications in a prospective cohort of patients who underwent real time ultrasound guided automated percutaneous renal biopsy of native kidney in a single nephrology center. Percutaneous renal biopsy is essential for diagnosis of many renal diseases. previous studies have revealed a variety of factors associated with bleeding complications of renal biopsy; however, data are not sufficient in the chinese population. we aimed to investigate the risk factors for severe post biopsy bleeding events in a large cohort of chinese patients. Conclusions less than 5% of kidney biopsies had bleeding complications requiring intervention. practitioners should carefully assess the risk benefit ratio of renal biopsy, particularly for patients with rheumatologic comorbidities and hypertension, given their higher bleeding complication rates. The primary indications for native prb is to evaluate proteinuria, microscopic hematuria, renal manifestations of systemic disease, and unexplained renal failure.5 the procedure is useful in diagnosis, prognosis, and management of nephropathies; however, despite technological advances, the procedure remains high risk for several reasons. bleeding complications are common due to the vascularity. Previous reports of incidence of major complications (mc) of kidney biopsy vary depending on definitions of mc, single or multicentre analysis, and prospective or retrospective data collection. we aimed to provide accurate, unbiased information about the incidence of mc by analysing 10 year data from a prospective national renal biopsy registry.

Subtracting Mixed Fractions Math Fun Math Resources Video Math Percutaneous renal biopsy is essential for diagnosis of many renal diseases. previous studies have revealed a variety of factors associated with bleeding complications of renal biopsy; however, data are not sufficient in the chinese population. we aimed to investigate the risk factors for severe post biopsy bleeding events in a large cohort of chinese patients. Conclusions less than 5% of kidney biopsies had bleeding complications requiring intervention. practitioners should carefully assess the risk benefit ratio of renal biopsy, particularly for patients with rheumatologic comorbidities and hypertension, given their higher bleeding complication rates. The primary indications for native prb is to evaluate proteinuria, microscopic hematuria, renal manifestations of systemic disease, and unexplained renal failure.5 the procedure is useful in diagnosis, prognosis, and management of nephropathies; however, despite technological advances, the procedure remains high risk for several reasons. bleeding complications are common due to the vascularity. Previous reports of incidence of major complications (mc) of kidney biopsy vary depending on definitions of mc, single or multicentre analysis, and prospective or retrospective data collection. we aimed to provide accurate, unbiased information about the incidence of mc by analysing 10 year data from a prospective national renal biopsy registry. Two reviewers independently selected studies evaluating the bleeding risk from renal biopsies performed in outpatient and inpatient settings and reviewed their full texts. the primary and secondary outcomes were risks of bleeding and major events (including mortality) following the procedure, respectively. Renal biopsies are done all over the world by nephrologists and radiologists for myriads of indications on a daily basis. they are unfortunately associated with several dreaded complications, the worst of which is the post biopsy bleed. the incidence of bleeding post biopsy has been reported to be between 0 6% in various studies. what is the current rate of bleed with the use of automated.

Subtracting Mixed Number Fractions The primary indications for native prb is to evaluate proteinuria, microscopic hematuria, renal manifestations of systemic disease, and unexplained renal failure.5 the procedure is useful in diagnosis, prognosis, and management of nephropathies; however, despite technological advances, the procedure remains high risk for several reasons. bleeding complications are common due to the vascularity. Previous reports of incidence of major complications (mc) of kidney biopsy vary depending on definitions of mc, single or multicentre analysis, and prospective or retrospective data collection. we aimed to provide accurate, unbiased information about the incidence of mc by analysing 10 year data from a prospective national renal biopsy registry. Two reviewers independently selected studies evaluating the bleeding risk from renal biopsies performed in outpatient and inpatient settings and reviewed their full texts. the primary and secondary outcomes were risks of bleeding and major events (including mortality) following the procedure, respectively. Renal biopsies are done all over the world by nephrologists and radiologists for myriads of indications on a daily basis. they are unfortunately associated with several dreaded complications, the worst of which is the post biopsy bleed. the incidence of bleeding post biopsy has been reported to be between 0 6% in various studies. what is the current rate of bleed with the use of automated.
Comments are closed.