How To Determine If A Sequence Converges By Rationalizing
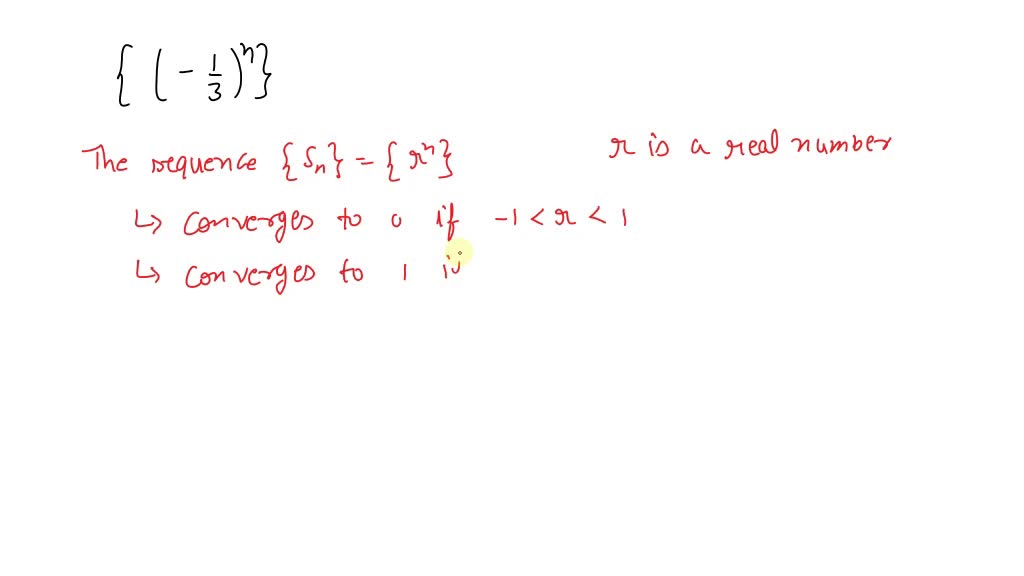
Solved Determine Whether The Given Sequence Converges If The Sequence In this video i will show you how to determine if a sequence converges by rationalizing if you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. So that's the real question: what does it mean for a sequence to converge? it's easy to bring a lot of tuition to this discussion, but our goal will be to precisely pinpoint exactly what it means for a sequence to converge.
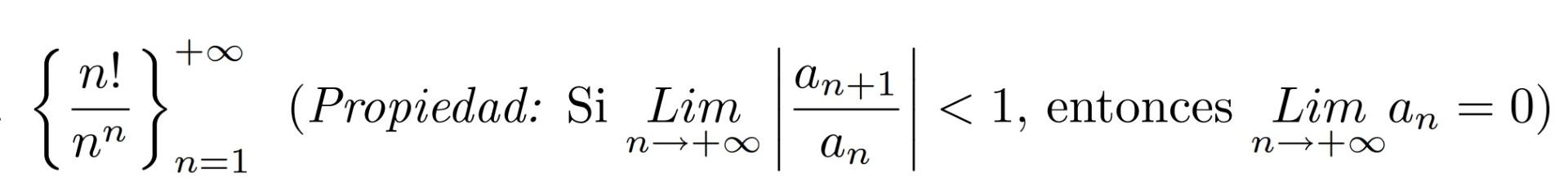
Solved Determine Whether The Given Sequence Converges If Chegg If we say that a sequence converges, it means that the limit of the sequence exists as n tends toward infinity. if the limit of the sequence as doesn’t exist, we say that the sequence diverges. a sequence always either converges or diverges, there is no other option. We will illustrate how partial sums are used to determine if an infinite series converges or diverges. we will also give the divergence test for series in this section. A sequence an a n is identical to a sequence bn b n if they both attain the same values in exactly the same order. if an a n and bn b n differ from each other in only a finite number of terms, then both sequences converge to the same value or they both diverge. Note the di erence between 1 and 1 is 2 which suggests we pick a tolerance < 2 to show the sequence does not converge to 1 as we want to isolate which value we are trying to get close to.
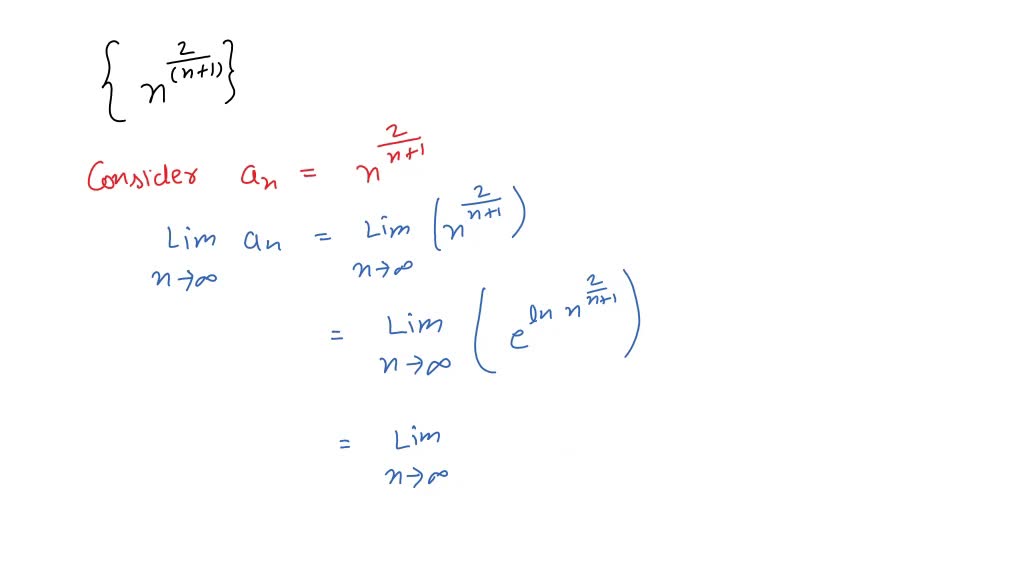
Solved Determine Whether The Given Sequence Converges If The Sequence A sequence an a n is identical to a sequence bn b n if they both attain the same values in exactly the same order. if an a n and bn b n differ from each other in only a finite number of terms, then both sequences converge to the same value or they both diverge. Note the di erence between 1 and 1 is 2 which suggests we pick a tolerance < 2 to show the sequence does not converge to 1 as we want to isolate which value we are trying to get close to. This page titled 5.3: real analysis convergent sequences is shared under a cc by nc sa 2.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by dave witte morris & joy morris. This article shows you how to prove convergence for recursively defined sequences, i.e. if there is only given and it is not known, what explicitly looks like. the monotonicity criterion will turn out very useful for this. we want to solve problems of the following kind:. My initial strategy was to use the monotone sequence theorem. it's obvious that each term is positive, so it is bounded below by 0 0. plugging in this sequence into desmos shows it appears to be decreasing (if m> n m> n, then am ≤an a m ≤ a n). where i struggle is proving that it is decreasing. Explore the essentials of sequence convergence, including definitions, key tests, ap calculus problems, to master limits and series.
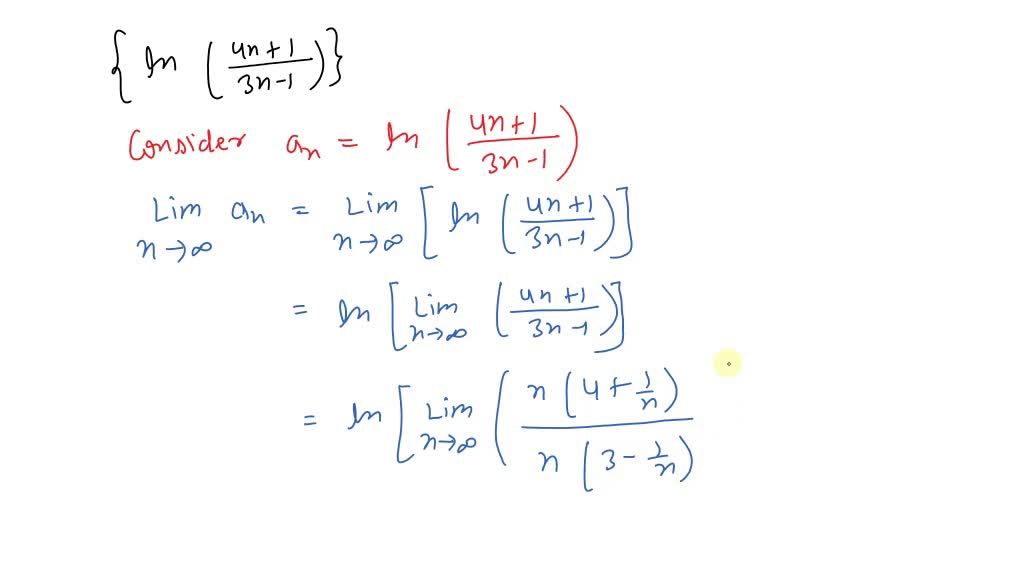
Solved Determine Whether The Given Sequence Converges If The Sequence This page titled 5.3: real analysis convergent sequences is shared under a cc by nc sa 2.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by dave witte morris & joy morris. This article shows you how to prove convergence for recursively defined sequences, i.e. if there is only given and it is not known, what explicitly looks like. the monotonicity criterion will turn out very useful for this. we want to solve problems of the following kind:. My initial strategy was to use the monotone sequence theorem. it's obvious that each term is positive, so it is bounded below by 0 0. plugging in this sequence into desmos shows it appears to be decreasing (if m> n m> n, then am ≤an a m ≤ a n). where i struggle is proving that it is decreasing. Explore the essentials of sequence convergence, including definitions, key tests, ap calculus problems, to master limits and series.
Comments are closed.