How Human Memory Works Encoding Storage And Retrieval
The Encoding Storage And Retrieval Of Human Memory By Michael The process by which our experiences become part of our memory involves three critical stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. these interrelated processes form the foundation of how we learn, adapt, and function in our daily lives. The steps involved in memory formation include encoding, storage, and recall (retrieval) in that order. amnesia is a phenomenon in which there is the problem in memory formation which can be due to trauma to the brain, certain diseases, or stressors.

Memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Encoding transforms incoming information into a form that can be processed by the brain. storage maintains that information over time. retrieval involves accessing and bringing stored information back into conscious awareness when needed. Encoding refers to the phase during which the brain is making a new memory. during encoding, our brain translates what we're experiencing into information and stores it in neural pathways between brain cells so that it can be recalled later. Encoding is the act of getting information into our memory system through automatic or effortful processing. storage is retention of the information, and retrieval is the act of getting information out of storage and into conscious awareness through recall, recognition, and relearning. Good encoding techniques include relating new information to what one already knows, forming mental images, and creating associations among information that needs to be remembered. the key to good retrieval is developing effective cues that will lead the rememberer back to the encoded information.
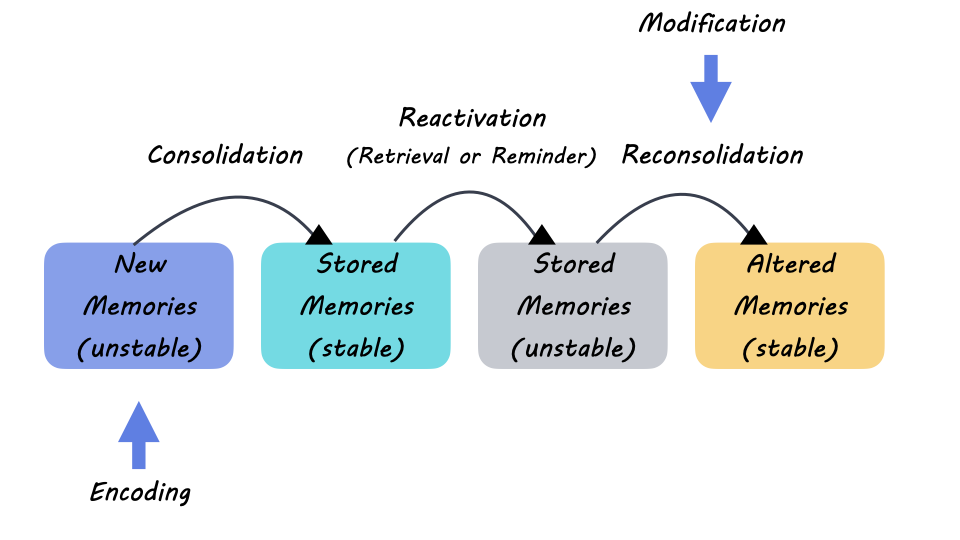
Memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Encoding is the act of getting information into our memory system through automatic or effortful processing. storage is retention of the information, and retrieval is the act of getting information out of storage and into conscious awareness through recall, recognition, and relearning. Good encoding techniques include relating new information to what one already knows, forming mental images, and creating associations among information that needs to be remembered. the key to good retrieval is developing effective cues that will lead the rememberer back to the encoded information. Human memory can be broadly classified into three main stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. encoding refers to the process of transforming sensory input into a format that can be stored in the brain. this can involve visual images, sounds, or meanings. Encoding is defined as the initial learning of information; storage refers to maintaining information over time; retrieval is the ability to access information when you need it. Understanding these three interconnected processes – encoding, storage, and retrieval – helps shed light on how our memory works. from the initial encoding of new experiences to their long term storage and eventual retrieval when needed, each step plays a crucial role in shaping our ability to learn and remember. Once information is encoded, it must be stored somewhere in the brain to be retrieved later. storage can be short term (a few seconds to a minute) or long term (days to decades). the transition from short term to long term memory is known as consolidation.
Comments are closed.