Homogeneous Coordinates Mike On Matlab Graphics

13 Homogeneous Coordinates For Computer Graphics We use them constantly in computer graphics, and they're the fundamental representation in the rendering library which underlies matlab's new graphics system. let's take a look at how homogeneous coordinates work, and why computer graphics programmers love them so much. Affine transformations 3d position : − 3x3 matrix represents linear transformations − scale, rotation, shear − 3d vector represents translation − using the homogeneous notation, all affine transformations are represented with one matrix vector multiplication.
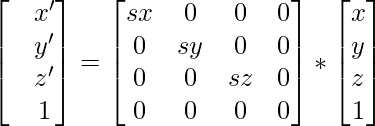
Computer Graphics Homogeneous Coordinates Geeksforgeeks You might wonder if we've lost the ability to do the kinds of transformations we learned above now that we're working in homogeneous coordinates. actually, they all remain available with easy modifications to what you already know. Points at infinity can be represented by finite coordinates used extensively in graphics because they perform translation, scaling, and rotation to implement matrix operations in some cases, homogeneous coordinates handle points at infinity. In homogeneous coordinate system, two dimensional coordinate positions (x, y) are represented by triple coordinates. homogeneous coordinates are generally used in design and construction applications. here we perform translations, rotations, scaling to fit the picture into proper position. In practice, homogeneous coordinates represent r2 by mapping each euclidean point (x’, y’) ̨ e2 to [x, y, w] ̨ e3 (w „ 0), which is a member of the equivalence class of points in r2.
Homogeneous Coordinates Mike On Matlab Graphics In homogeneous coordinate system, two dimensional coordinate positions (x, y) are represented by triple coordinates. homogeneous coordinates are generally used in design and construction applications. here we perform translations, rotations, scaling to fit the picture into proper position. In practice, homogeneous coordinates represent r2 by mapping each euclidean point (x’, y’) ̨ e2 to [x, y, w] ̨ e3 (w „ 0), which is a member of the equivalence class of points in r2. We’ll begin the study of homogeneous coordinates by describing a set of problems from three dimensional computer graphics that at first seem to have unrelated solutions. Download and share free matlab code, including functions, models, apps, support packages and toolboxes. That representation can also be extended by representing geometry in different ways such as using homogeneous coordinates, or positional encoding. we will discuss homogeneous coordinates in this chapter. the previous two representations are not the only ways in which we can represent images. This study explores the practical applications of homogeneous coordinates within the matlab environment, leveraging its matrix manipulation capabilities to implement these transformations efficiently.
Comments are closed.