H2o2 Decomposition Chemistry Science Experiments Lab Boom

Explosive Boom Lab Kids Home Science Experiments Kit The structure of $\ce {h2o2}$ is $\ce {h o o h}$, and an $\ce { o o }$ functional group is called a peroxide, by definition. the peroxide functional group is attached to a hydrogen atom, so it's called hydrogen peroxide. calling it a dihydrogen dioxide (hydrate is water, not hydrogen) would not only be long but also not show the type of reactivity the substance has. so it's just more. Is there a complete list of all the half equations for $\ce {h2o2}$ both oxidation and reduction, in acidic and alkaline conditions? i've looked on the internet but can't seem to find a list with all of them.

Lab 8 Decomposition Of Hydrogen Peroxide Austin Community College When exposed to uv light, hydrogen peroxide decomposes into $\ce {h2o}$ and $\ce {o}$. why does this happen and more importantly how? is the energy from light absorbed by the bonds which are specific. When hydrogen peroxide is mixed with potassium permanganate, oxygen gas and water vapour are formed, according to the reaction (source): $$\\ce{2mno4 3h2o2 > 2mno2 2h2o 3o2 2oh }$$ this. In basic medium: $\ce {h2o2 2e > 2oh }$ i was unable to find any pattern in all of the reactions i studied above (except for potassium ferrocyanide, for which the medium triggers the electron addition removal) to recognize when hydrogen peroxide behaves as an oxidising agent and when it behaves as a reducing agent. $\ce {h2o2}$ will homolytically cleave for form two $\ce {.oh}$ radicals. radicals are very reactive and will start a chain reaction, but ultimately you will end up with water and oxygen products from $\ce {h2o2}$. (why does it form two hydroxy radicals? because the o o single bond is weak and unstable see mo theory) how do we know this?.

Lab 4 Decomposition Of Hydrogen Peroxide Docx Kinetics Decomposition In basic medium: $\ce {h2o2 2e > 2oh }$ i was unable to find any pattern in all of the reactions i studied above (except for potassium ferrocyanide, for which the medium triggers the electron addition removal) to recognize when hydrogen peroxide behaves as an oxidising agent and when it behaves as a reducing agent. $\ce {h2o2}$ will homolytically cleave for form two $\ce {.oh}$ radicals. radicals are very reactive and will start a chain reaction, but ultimately you will end up with water and oxygen products from $\ce {h2o2}$. (why does it form two hydroxy radicals? because the o o single bond is weak and unstable see mo theory) how do we know this?. Manganese dioxide catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. but what are the intermediates in this catalyzed reaction?. The decomposition of h2o2 is complex and has been the source of several studies. on iron oxide surface, here is a `catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on iron oxide: kinetics, mechanism, and implications’. some selected quotes: "as depicted in figure 2, the decomposition rate of h2o2 appears to be independent of the goethite particle. I saw a reaction by chemicalforce on where he decomposed $\ce {h2o2}$ into $\ce {h2o}$ and $\ce {o2}$ using potassium permanganate. the permanganate is a catalyst in the reaction. Is it possible to oxidize ethanol to acetic acid with hydrogen peroxide and if yes then under what circumstances? i tried it in room temperature but either concentration was too small (of hydrogen.
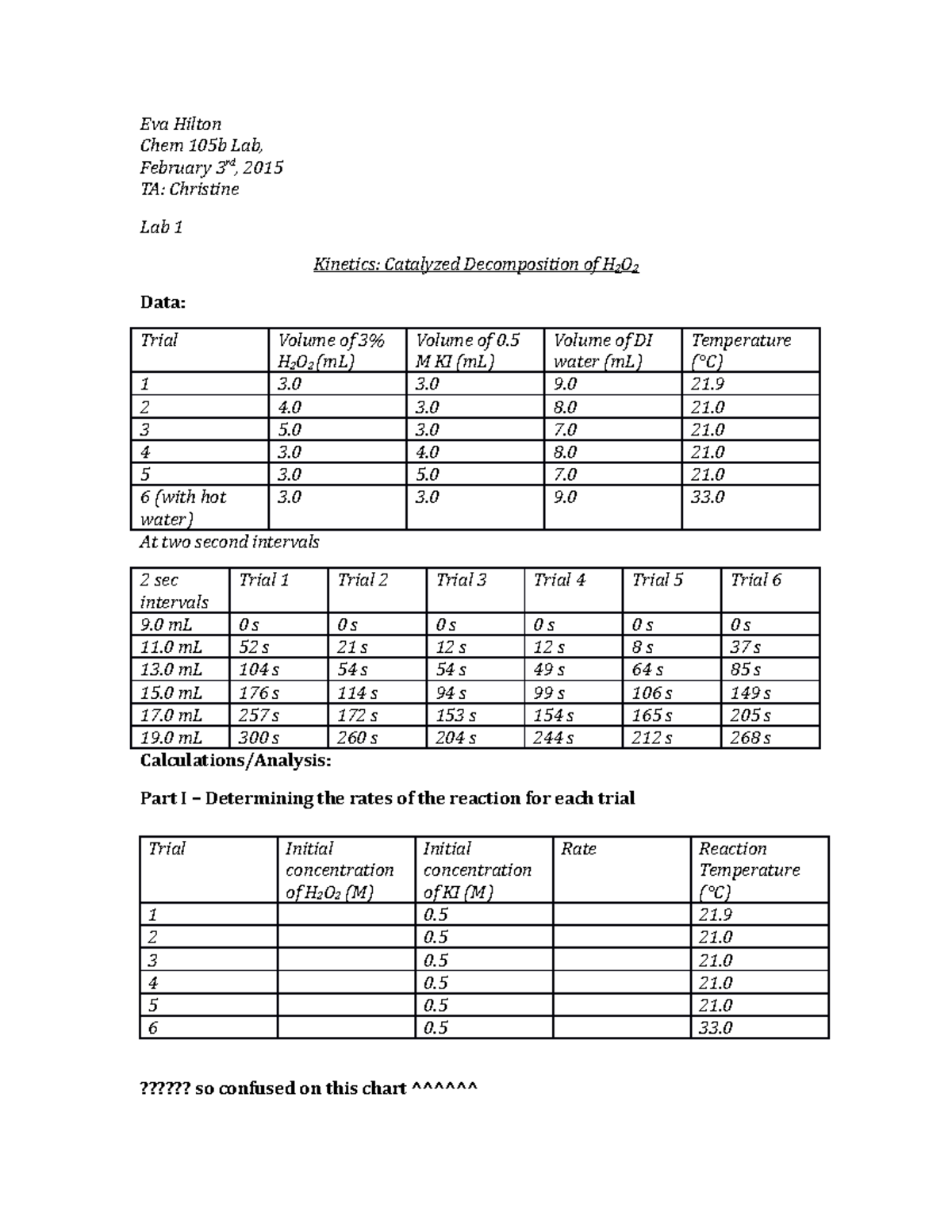
Chem 105b Lab Kinetics Of H2o2 Decomposition Studocu Manganese dioxide catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. but what are the intermediates in this catalyzed reaction?. The decomposition of h2o2 is complex and has been the source of several studies. on iron oxide surface, here is a `catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on iron oxide: kinetics, mechanism, and implications’. some selected quotes: "as depicted in figure 2, the decomposition rate of h2o2 appears to be independent of the goethite particle. I saw a reaction by chemicalforce on where he decomposed $\ce {h2o2}$ into $\ce {h2o}$ and $\ce {o2}$ using potassium permanganate. the permanganate is a catalyst in the reaction. Is it possible to oxidize ethanol to acetic acid with hydrogen peroxide and if yes then under what circumstances? i tried it in room temperature but either concentration was too small (of hydrogen.

Experiment E Short Lab Report Experiment E Kinetics Of Catalyzed I saw a reaction by chemicalforce on where he decomposed $\ce {h2o2}$ into $\ce {h2o}$ and $\ce {o2}$ using potassium permanganate. the permanganate is a catalyst in the reaction. Is it possible to oxidize ethanol to acetic acid with hydrogen peroxide and if yes then under what circumstances? i tried it in room temperature but either concentration was too small (of hydrogen.

H2o2 Decomposition Pdf Hydrogen Peroxide Industrial Processes
Comments are closed.