Git Merge Vs Rebase

Git Merge Vs Rebase When working with git, two common strategies for integrating changes from different branches are merging and rebasing. both techniques serve the purpose of combining code from multiple branches, but they do so in different ways. When you’re working on a project in git, you’ll eventually need to incorporate changes from one branch into another. you have two main tools at your disposal: git merge and git rebase. although they seem similar, they function differently and can shape your project history in distinct ways.
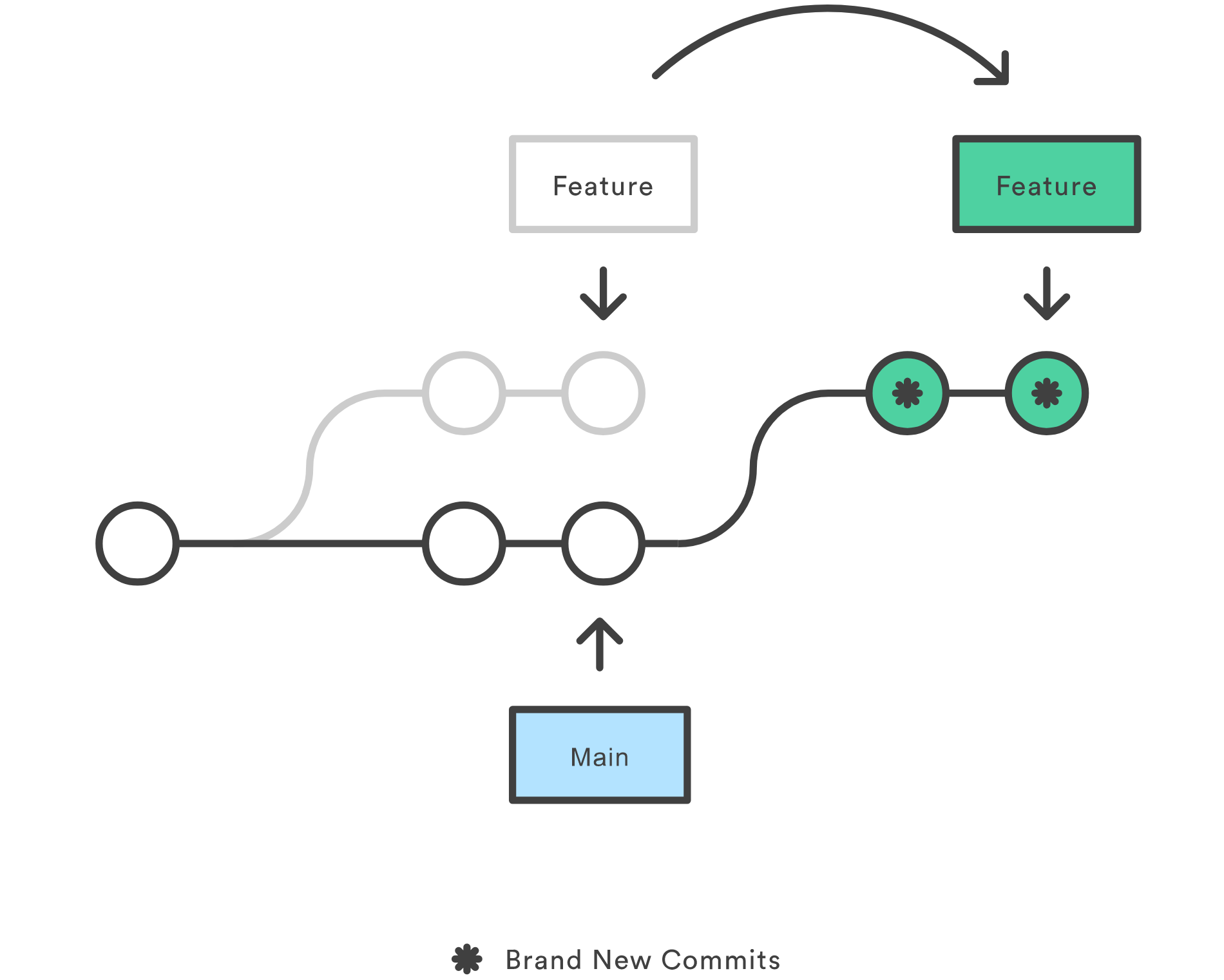
Net Handbook Git Merge Vs Rebase When we use git merge, a merge commit is created. this commit has two parent commits; therefore, if you use certain ui clients to view your git history, you will see something like this: if you. Select topic area question body i’ve been using git for a while, but i still get confused about when to use git merge vs git rebase. both seem to combine changes from one branch into another, but people say they have different use cases. can someone explain in simple terms the actual difference and maybe give examples of when one is better than the other?. Safe force push: git push force with lease merge with explicit commit: git merge no ff feature branch abort operations: git rebase abort git merge abort the golden rule never rebase branches that other people are working on. rebasing rewrites commit history (new hashes). if others have those commits, you’ll create conflicts for everyone. A detailed comparison of git merge and git rebase. the article provides a step by step guide on how to integrate a feature branch into the main branch, explains the key differences, and offers guidance on when to use each method.
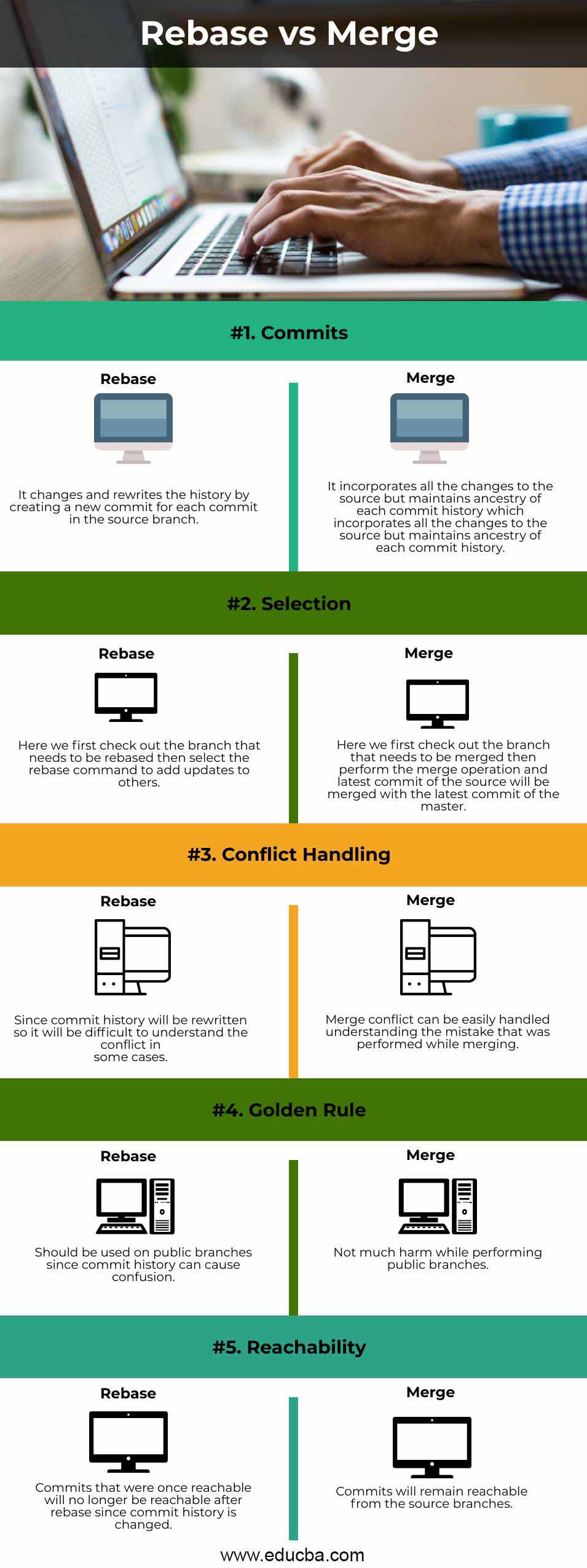
Git Rebase Vs Merge Top 5 Differences With Infographics Safe force push: git push force with lease merge with explicit commit: git merge no ff feature branch abort operations: git rebase abort git merge abort the golden rule never rebase branches that other people are working on. rebasing rewrites commit history (new hashes). if others have those commits, you’ll create conflicts for everyone. A detailed comparison of git merge and git rebase. the article provides a step by step guide on how to integrate a feature branch into the main branch, explains the key differences, and offers guidance on when to use each method. Merge preserves the commit history by creating a new merge commit, making it easier to track changes whereas rebase rewrites history by applying commits sequentially. choosing between them depends on project workflow and collaboration needs. When working with git, both rebase and merge are used to integrate changes from one branch into another—but they do so in fundamentally different ways. git merge combines the histories of two branches by creating a new "merge commit" that ties them together. Learn the key differences between git rebase vs. merge, when to use each, and how to keep your project history clean and collaboration smooth.
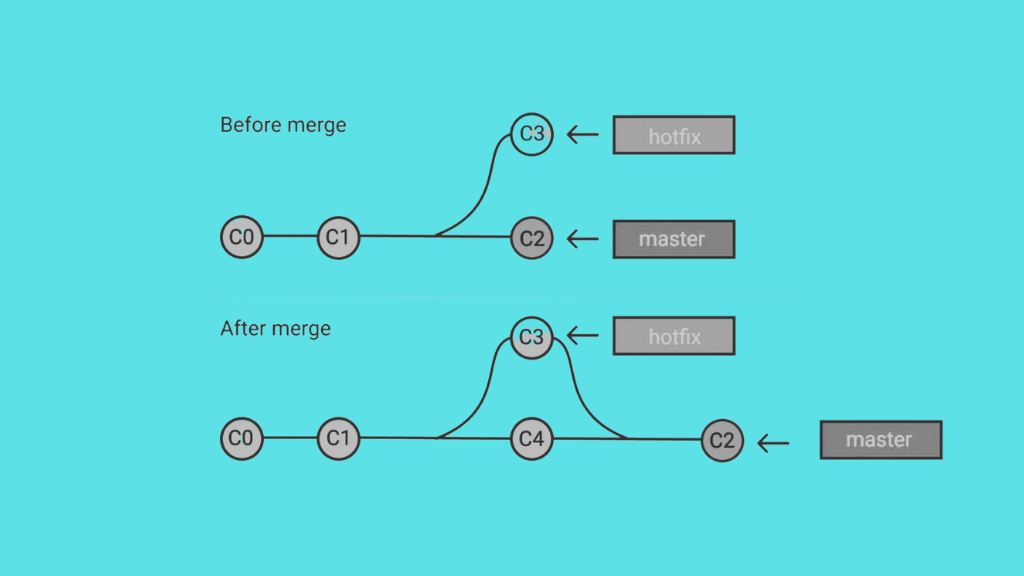
Git Rebase Vs Merge A Detailed Insight Jonas Cleveland Merge preserves the commit history by creating a new merge commit, making it easier to track changes whereas rebase rewrites history by applying commits sequentially. choosing between them depends on project workflow and collaboration needs. When working with git, both rebase and merge are used to integrate changes from one branch into another—but they do so in fundamentally different ways. git merge combines the histories of two branches by creating a new "merge commit" that ties them together. Learn the key differences between git rebase vs. merge, when to use each, and how to keep your project history clean and collaboration smooth.
Comments are closed.