Future Workplace 2025 Pdf Online And Offline Employment

Future Workplace 2025 Pdf Online And Offline Employment The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: an asynchronous operation (created via std::async, std::packaged task, or std::promise) can provide a std::future object to the creator of that asynchronous operation. the creator of the asynchronous operation can then use a variety of methods to query, wait for, or extract a value from the std. The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). right after calling this function, valid () is false.
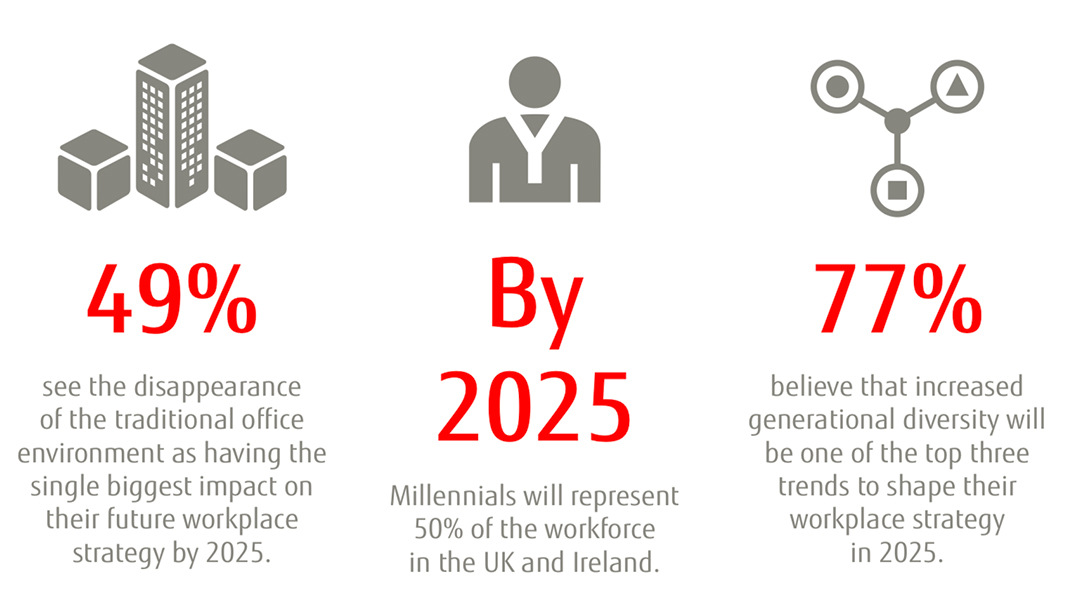
Future Workplace 2025 Future Workplace 2025 Fujitsu Uk I get this warning while testing in spring boot: mockito is currently self attaching to enable the inline mock maker. this will no longer work in future releases of the jdk. please add mockito as an. If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. this function may block for longer than timeout duration due to scheduling or resource contention delays. the standard recommends that a steady clock is used to measure the duration. Checks if the future refers to a shared state. this is the case only for futures that were not default constructed or moved from (i.e. returned by std::promise::get future (), std::packaged task::get future () or std::async ()) until the first time get () or share () is called. 320 when i run the program, pandas gives 'future warning' like below every time. d:\python\lib\site packages\pandas\core\frame.py:3581: futurewarning: rename with inplace=true will return none from pandas 0.11 onward " from pandas 0.11 onward", futurewarning) i got the message, but i just want to stop pandas showing such message again and again.

Future Of Work Pdf Creativity New Media Checks if the future refers to a shared state. this is the case only for futures that were not default constructed or moved from (i.e. returned by std::promise::get future (), std::packaged task::get future () or std::async ()) until the first time get () or share () is called. 320 when i run the program, pandas gives 'future warning' like below every time. d:\python\lib\site packages\pandas\core\frame.py:3581: futurewarning: rename with inplace=true will return none from pandas 0.11 onward " from pandas 0.11 onward", futurewarning) i got the message, but i just want to stop pandas showing such message again and again. A future statement is a directive to the compiler that a particular module should be compiled using syntax or semantics that will be available in a specified future release of python. the future statement is intended to ease migration to future versions of python that introduce incompatible changes to the language. it allows use of the new features on a per module basis before the release in. 2) move constructor. constructs a std::future with the shared state of other using move semantics. after construction, other.valid() == false. The promise is the "push" end of the promise future communication channel: the operation that stores a value in the shared state synchronizes with (as defined in std::memory order) the successful return from any function that is waiting on the shared state (such as std::future::get). The first part is easy: you can use annotations because annotations have existed since python 3.0, you don't need to import anything from future to use them what you're importing if you do from future import annotations is postponed annotations. the postponed annotations feature means that you can use something in an annotation even if it hasn't been defined yet try the following: def.

The Future Of Work Pdf Telecommuting Employment A future statement is a directive to the compiler that a particular module should be compiled using syntax or semantics that will be available in a specified future release of python. the future statement is intended to ease migration to future versions of python that introduce incompatible changes to the language. it allows use of the new features on a per module basis before the release in. 2) move constructor. constructs a std::future with the shared state of other using move semantics. after construction, other.valid() == false. The promise is the "push" end of the promise future communication channel: the operation that stores a value in the shared state synchronizes with (as defined in std::memory order) the successful return from any function that is waiting on the shared state (such as std::future::get). The first part is easy: you can use annotations because annotations have existed since python 3.0, you don't need to import anything from future to use them what you're importing if you do from future import annotations is postponed annotations. the postponed annotations feature means that you can use something in an annotation even if it hasn't been defined yet try the following: def.

The Future Of Work In 2025 The promise is the "push" end of the promise future communication channel: the operation that stores a value in the shared state synchronizes with (as defined in std::memory order) the successful return from any function that is waiting on the shared state (such as std::future::get). The first part is easy: you can use annotations because annotations have existed since python 3.0, you don't need to import anything from future to use them what you're importing if you do from future import annotations is postponed annotations. the postponed annotations feature means that you can use something in an annotation even if it hasn't been defined yet try the following: def.
Comments are closed.