Frequent Alterations Arising In Breast And Ovarian Tumors From

Frequent Alterations Arising In Breast And Ovarian Tumors From Germline mutations in brca1 and brca2 (brca) genes confer high risk of developing cancer, especially breast and ovarian tumors. since the cloning of these tumor suppressor genes over two decades ago, a significant amount of research has been done. Germline mutations in brca1 and brca2 (brca) genes confer high risk of developing cancer, especially breast and ovarian tumors. since the cloning of these tumor suppressor genes over two.

Heterogeneous Genetic Alterations In Mucinous Ovarian Tumors A fact sheet about the brca1 and brca2 genes, what to do if a person tests positive for alterations in one of these genes, and consequences of genetic testing. Two highly penetrant genes that confer greatly increased risk of both breast and ovarian cancer have thus far been identified; brca1 and brca2 which confer a 40% and 15% lifetime risk of ovarian cancer, respectively [5–9]. Germline mutations affecting a single copy of the breast cancer genes brca1 or brca2 significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer (reviewed in nathanson et al., 2001; rahman and stratton, 1998; welcsh and king, 2001). Although hereditary breast and ovarian cancer elevate bc risk, over half of the genetic susceptibility to bc remains unexplained. given the considerable diversity among bc patients, the occurrence and genetic susceptibility of fbc vary based on race and geography.

Heterogeneous Genetic Alterations In Mucinous Ovarian Tumors Germline mutations affecting a single copy of the breast cancer genes brca1 or brca2 significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer (reviewed in nathanson et al., 2001; rahman and stratton, 1998; welcsh and king, 2001). Although hereditary breast and ovarian cancer elevate bc risk, over half of the genetic susceptibility to bc remains unexplained. given the considerable diversity among bc patients, the occurrence and genetic susceptibility of fbc vary based on race and geography. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (hboc) syndrome is most commonly characterized by deleterious germline mutations in brca1 and brca2. hboc patients are prone to the development of malignant neoplasms in multiple organs including the breast, ovary, and fallopian tube. Breast and ovarian cancer are present in several autosomal dominant cancer syndromes, although they are most strongly associated with highly penetrant germline pathogenic variants in brca1 and brca2. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (hboc) syndrome is most commonly characterized by deleterious germline mutations in brca1 and brca2. hboc patients are prone to the development of malignant neoplasms in multiple organs including the breast, ovary, and fallopian tube. The remaining 90% of breast cancers are due to acquired somatic genetic and epigenetic alterations. a heterogeneous set of somatic alterations, including mutations and gene amplification, are reported to be involved in the etiology of breast cancer.
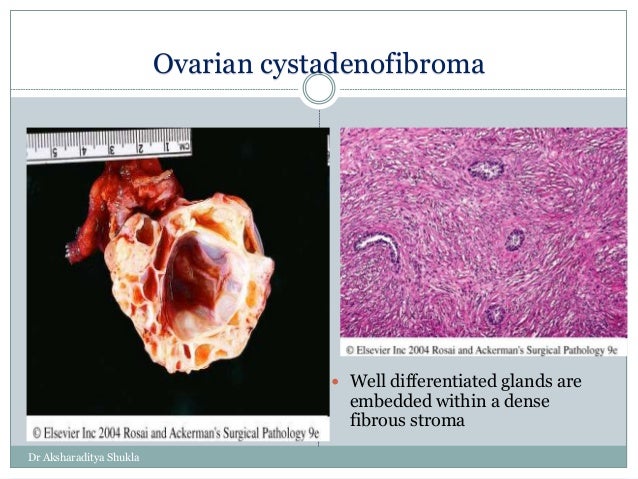
Ovarian Tumors I Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (hboc) syndrome is most commonly characterized by deleterious germline mutations in brca1 and brca2. hboc patients are prone to the development of malignant neoplasms in multiple organs including the breast, ovary, and fallopian tube. Breast and ovarian cancer are present in several autosomal dominant cancer syndromes, although they are most strongly associated with highly penetrant germline pathogenic variants in brca1 and brca2. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (hboc) syndrome is most commonly characterized by deleterious germline mutations in brca1 and brca2. hboc patients are prone to the development of malignant neoplasms in multiple organs including the breast, ovary, and fallopian tube. The remaining 90% of breast cancers are due to acquired somatic genetic and epigenetic alterations. a heterogeneous set of somatic alterations, including mutations and gene amplification, are reported to be involved in the etiology of breast cancer.

Ovarian Tumors Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (hboc) syndrome is most commonly characterized by deleterious germline mutations in brca1 and brca2. hboc patients are prone to the development of malignant neoplasms in multiple organs including the breast, ovary, and fallopian tube. The remaining 90% of breast cancers are due to acquired somatic genetic and epigenetic alterations. a heterogeneous set of somatic alterations, including mutations and gene amplification, are reported to be involved in the etiology of breast cancer.

Benign Ovarian Tumors Pptbenign Ovarian Tumors Ppt
Comments are closed.