Flatten Pdf Forms Using Unipdf

Unidoclib On Linkedin Flatten Pdf Forms Using Unipdf If your list of lists comes from a nested list comprehension, the problem can be solved more simply directly by fixing the comprehension; please see how can i get a flat result from a list comprehension instead of a nested list?. the most popular solutions here generally only flatten one "level" of the nested list. see flatten an irregular (arbitrarily nested) list of lists for solutions that. 11 often, when numpy has seemingly duplicate functions, there often ends up being some sort of unique purpose for one or the other. i am trying to figure out if there are any situations where flatten() should be used instead of reshape( 1).
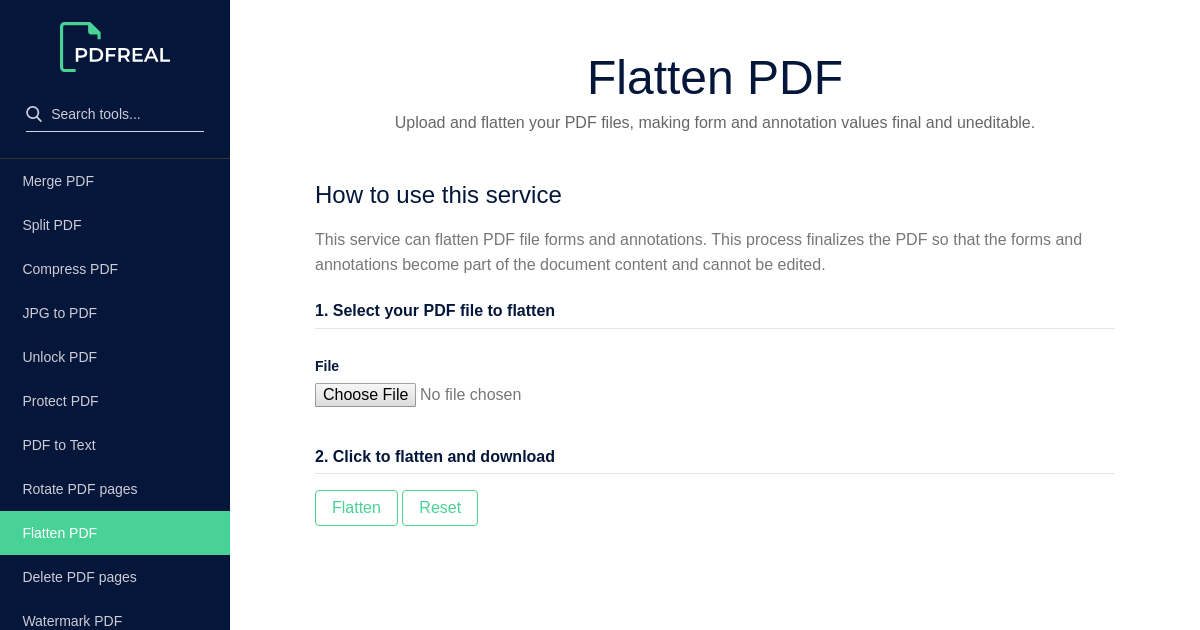
Pdf Real Online Editor Tool To Flatten Your Pdf File Online We recently purchased adobe acrobat pro dc and i'm trying to figure out how to take a document that i added a stamp to and flatten it so our users cannot delete the stamp from it. i have found the 'flatten' option but it is greyed out. the only option in the menu available is 'import as layer'. h. The role of the flatten layer in keras is super simple: a flatten operation on a tensor reshapes the tensor to have the shape that is equal to the number of elements contained in tensor non including the batch dimension. note: i used the model.summary() method to provide the output shape and parameter details. Hi everyone, i have a pdf form that i've created for my team to help make creating contracts easier. essentially what it does is it has a bunch of form fields on page 1 that fill in all the appropriate information on all the other pages. i've then created buttons that print just the pages we need,. Creating a submit button that will rename, flatten, hide button, save a copy, and email new file.
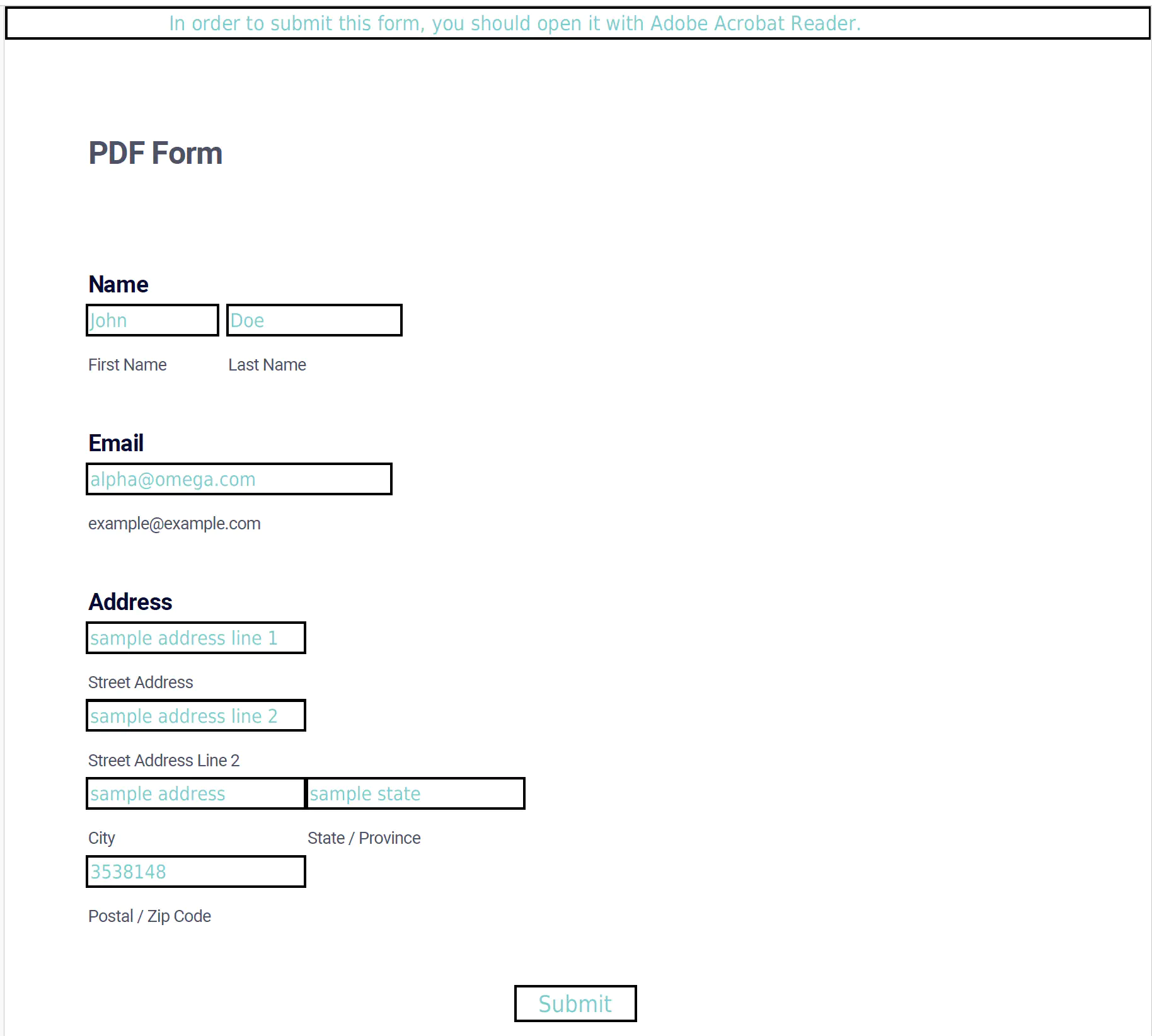
Fill Flatten Forms With Appearance Unidoc Hi everyone, i have a pdf form that i've created for my team to help make creating contracts easier. essentially what it does is it has a bunch of form fields on page 1 that fill in all the appropriate information on all the other pages. i've then created buttons that print just the pages we need,. Creating a submit button that will rename, flatten, hide button, save a copy, and email new file. I have seen various programs using matplotlib that uses the axes.flat function, like this code: for i, ax in enumerate (axes.flat): what does this do?. Here flatten demonstrates piecewise linear complexity which can be reasonably explained by it making a copy of the initial array compare to constant complexities of ravel and reshape that return a view. it's also worth noting that, quite predictably, converting the outputs .tolist() evens out the performance of all three to equally linear. I think the results here for the parallelstream are a little misleading. at a certain collection size, the benefit of parallel processing will outweigh the overhead needed for creating multiple threads, and delegating actions to them. the map you are testing with doesn't even come close to that threshold. in a real world scenario where the map could have thousands of value collections, each. 46 you might need to check out numpy.flatten and numpy.ravel, both return a 1 d array from an n d array. furthermore, if you're not going to modify the returned 1 d array, i suggest you use numpy.ravel, since it doesn't make a copy of the array, but just return a view of the array, which is much faster than numpy.flatten.
Flatten Pdf Online Layers Form Fields Annotation Avepdf I have seen various programs using matplotlib that uses the axes.flat function, like this code: for i, ax in enumerate (axes.flat): what does this do?. Here flatten demonstrates piecewise linear complexity which can be reasonably explained by it making a copy of the initial array compare to constant complexities of ravel and reshape that return a view. it's also worth noting that, quite predictably, converting the outputs .tolist() evens out the performance of all three to equally linear. I think the results here for the parallelstream are a little misleading. at a certain collection size, the benefit of parallel processing will outweigh the overhead needed for creating multiple threads, and delegating actions to them. the map you are testing with doesn't even come close to that threshold. in a real world scenario where the map could have thousands of value collections, each. 46 you might need to check out numpy.flatten and numpy.ravel, both return a 1 d array from an n d array. furthermore, if you're not going to modify the returned 1 d array, i suggest you use numpy.ravel, since it doesn't make a copy of the array, but just return a view of the array, which is much faster than numpy.flatten.
Comments are closed.