Figure 2 From Language Model Decoding As Likelihood Utility Alignment

Underline Language Model Decoding As Likelihood Utility Alignment Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide the first empirical evidence supporting the proposed taxonomy, and a set of principles to structure reasoning when choosing a decoding algorithm. When ti is the only cause of mis alignment, the likelihood is a strong predictor of utility; then, likelihood based decoding algorithms are expected to retrieve high utility outputs.
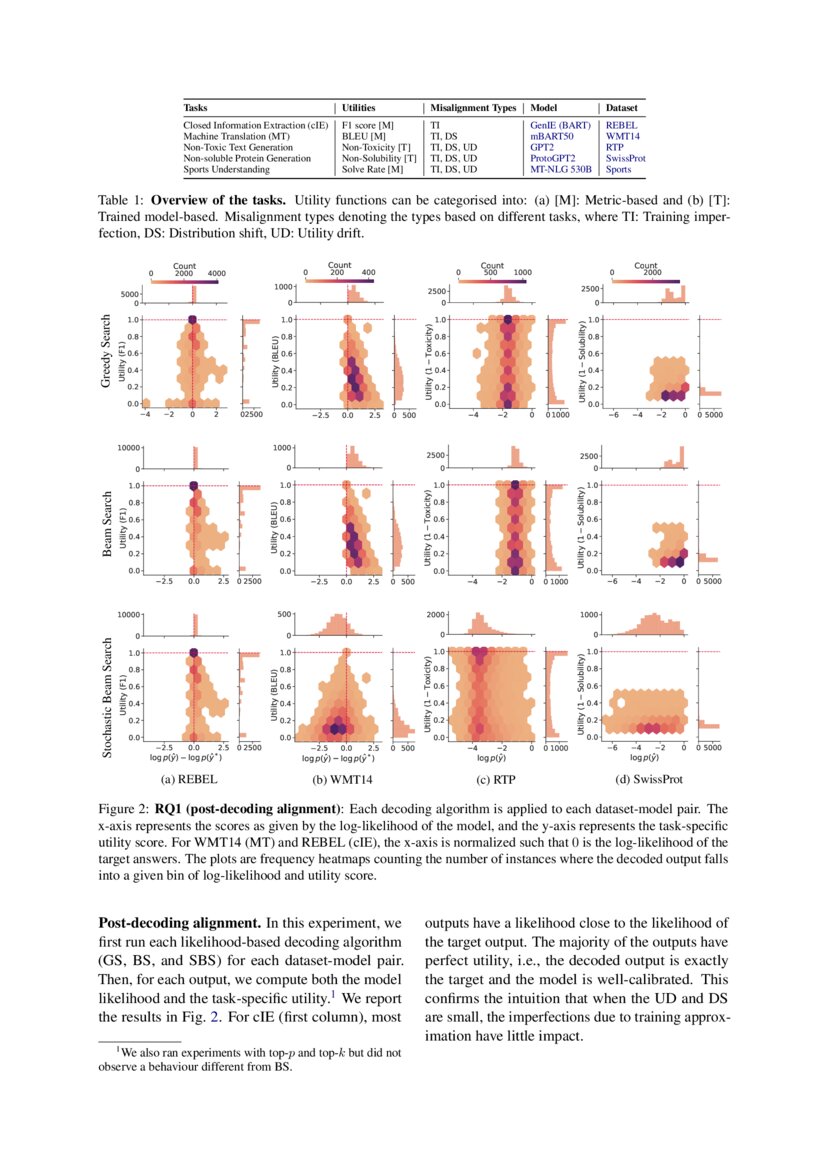
Language Model Decoding As Likelihood Utility Alignment Deepai Figure 2: rq1 (post decoding alignment): each decoding algorithm is applied to each dataset model pair. for each subplot, the x axis represents the outputs’ log likelihood under the model, and the y axis the output’s taskspecific utility score. Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide the first empirical evidence supporting the proposed. To better structure the discussion, we introduce a taxonomy that groups decoding strategies based on their implicit assumptions about how well the model’s likelihood is aligned with the. Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide empirical evidence supporting the proposed taxonomy and a set of principles to structure reasoning when choosing a decoding algorithm.

Pdf Language Model Decoding As Likelihood Utility Alignment To better structure the discussion, we introduce a taxonomy that groups decoding strategies based on their implicit assumptions about how well the model’s likelihood is aligned with the. Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide empirical evidence supporting the proposed taxonomy and a set of principles to structure reasoning when choosing a decoding algorithm. We argue that the misalignment between the model’s likelihood and the task specific notion of utility is the key factor to understanding the effectiveness of decoding algorithms. Figure 2: rq1 (post decoding alignment): each decoding algorithm is applied to each dataset model pair. for each subplot, the x axis represents the outputs’ log likelihood under the model, and the y axis the output’s task specific utility score. Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide empirical evidence supporting the proposed taxonomy and a set of principles to structure reasoning when choosing a decoding algorithm. Axis is the model’s log likelihood. the plots are generated as fol lows: (i) take the decoded outputs from fig. 2 from bs with their log likelihood score and utility score, which.

Figure 2 From Language Model Decoding As Likelihood Utility Alignment We argue that the misalignment between the model’s likelihood and the task specific notion of utility is the key factor to understanding the effectiveness of decoding algorithms. Figure 2: rq1 (post decoding alignment): each decoding algorithm is applied to each dataset model pair. for each subplot, the x axis represents the outputs’ log likelihood under the model, and the y axis the output’s task specific utility score. Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide empirical evidence supporting the proposed taxonomy and a set of principles to structure reasoning when choosing a decoding algorithm. Axis is the model’s log likelihood. the plots are generated as fol lows: (i) take the decoded outputs from fig. 2 from bs with their log likelihood score and utility score, which.
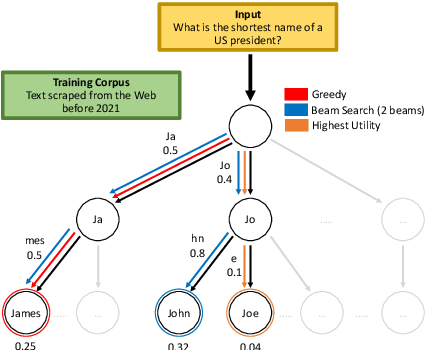
Figure 2 From Language Model Decoding As Likelihood Utility Alignment Specifically, by analyzing the correlation between the likelihood and the utility of predictions across a diverse set of tasks, we provide empirical evidence supporting the proposed taxonomy and a set of principles to structure reasoning when choosing a decoding algorithm. Axis is the model’s log likelihood. the plots are generated as fol lows: (i) take the decoded outputs from fig. 2 from bs with their log likelihood score and utility score, which.

Enhancing Language Model Alignment Using Language Based Feedback A
Comments are closed.