Explain 3 Tier Architecture For A Dbms Why Mapping Is Required In

Three Tier Dbms Architecture Pdf Databases Conceptual Model In this article, we will explain the details of the 3 tier architecture in dbms, explaining each of its components, the role it plays in application development, and the key benefits it offers for building robust, secure, and maintainable systems. The idea of a three tier dbms architecture may sound familiar to application developers, but it's not quite the same thing. we'll explain this distinction below.
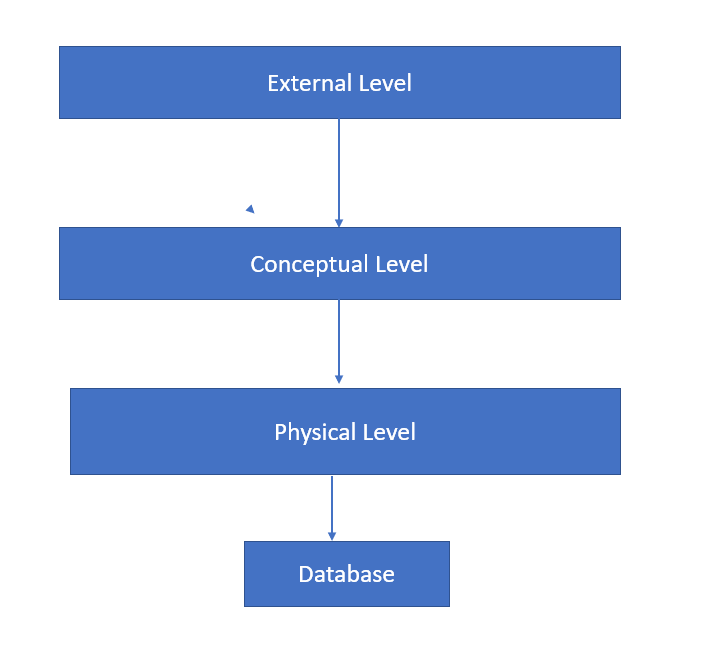
Explain 3 Tier Architecture For A Dbms Why Mapping Is Required In Among the myriad of architectures available, the 3 tier database architecture stands out as a popular and effective framework. this article aims to explain the 3 tier database architecture in simple terms, revealing its components, functionalities, and advantages. What is three tier architecture in dbms? three tier architecture in dbms divides the database system into three layers, each responsible for specific tasks: presentation layer (client tier): manages user interfaces. application layer (business logic tier): processes logic and interactions. Efficient in performance: a good dbms architecture improves performance by separating tasks. in a 3 tier setup, the application server handles business logic, reducing the load on the database server and speeding up overall processing. secure: architecture defines clear access rules. The framework of this type of architecture includes an external schema, a conceptual level, an internal schema, and then the database itself. the various levels of the database are mapped, which leads to the transformation of response and request in the database.
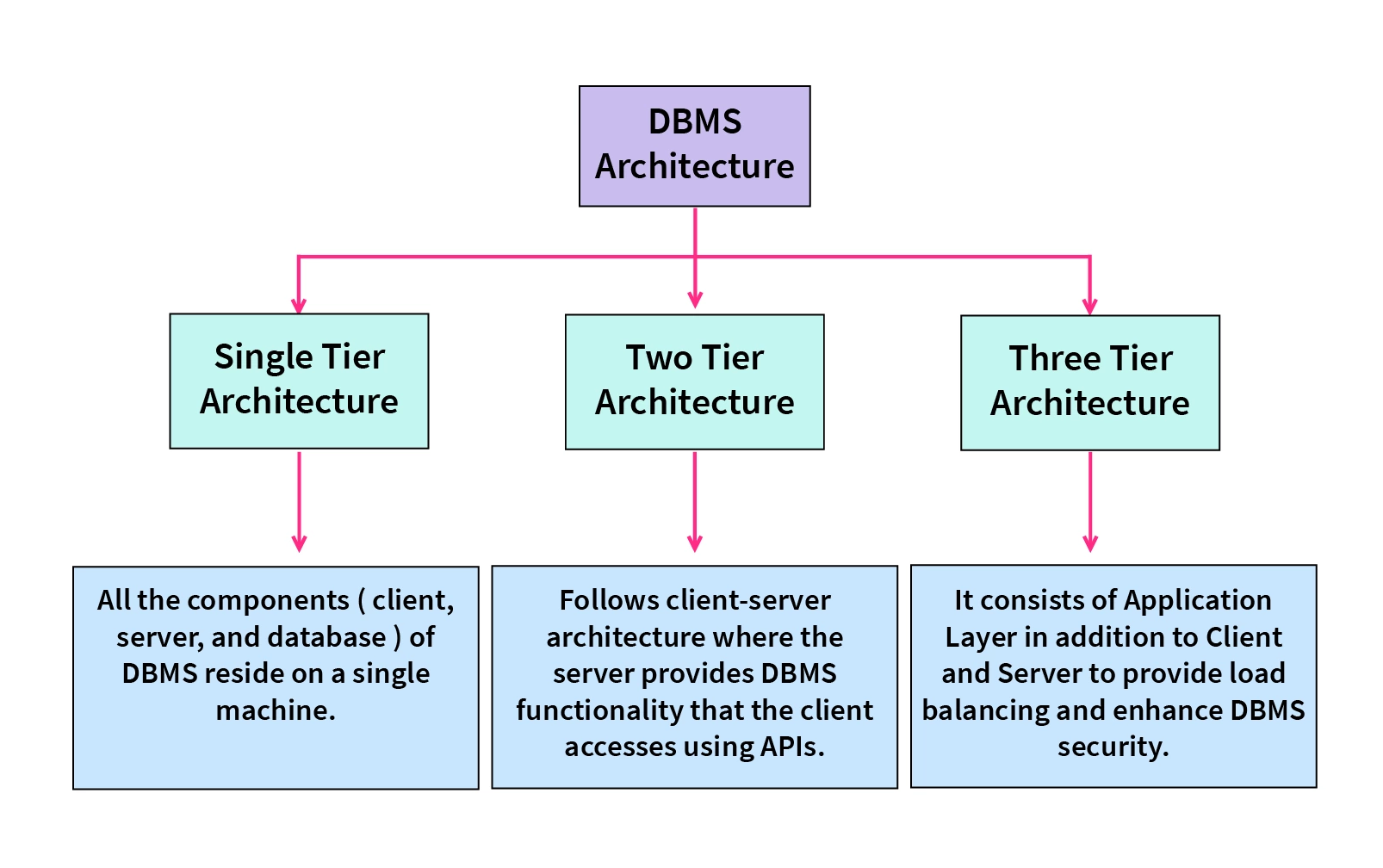
Explain 3 Tier Architecture For A Dbms Why Mapping Is Required In Efficient in performance: a good dbms architecture improves performance by separating tasks. in a 3 tier setup, the application server handles business logic, reducing the load on the database server and speeding up overall processing. secure: architecture defines clear access rules. The framework of this type of architecture includes an external schema, a conceptual level, an internal schema, and then the database itself. the various levels of the database are mapped, which leads to the transformation of response and request in the database. The following diagram shows the three level architecture of the dbms (database management system). mapping is used to make a connection between all three levels of the database. 3 tier architecture in dbms (database management system) is explained in this page along with the components, example, purpose and demerits. The 3 tier architecture is a widely used design pattern in database management systems (dbms) that enhances scalability, modularity, and maintenance. by dividing the system into three logical layers, this architecture ensures a clear separation of concerns, enabling better management and efficiency. The 3 tier architecture separates its tiers from each other based on the complexity of the users and how they use the data present in the database. it is the most widely used architecture to design a dbms.
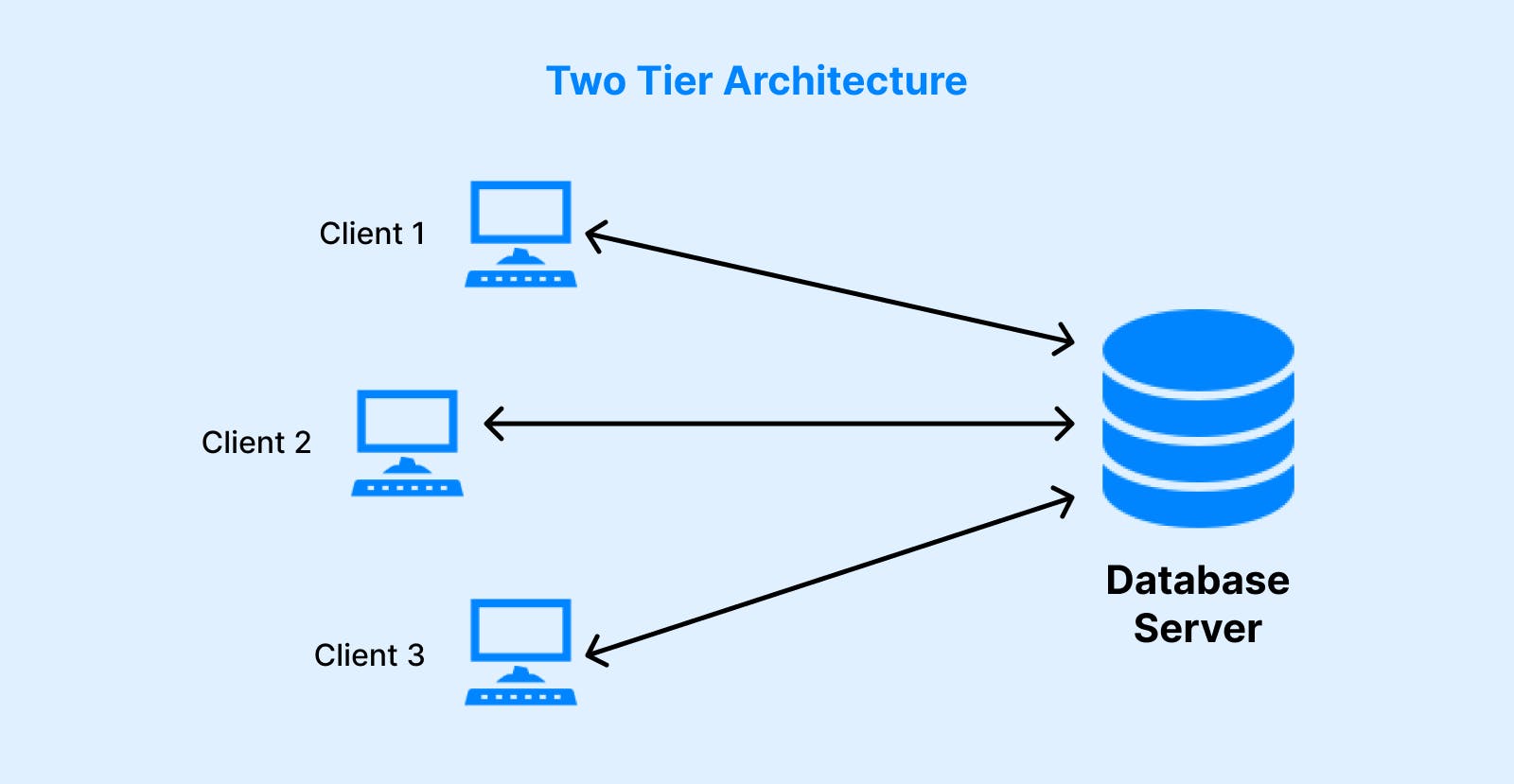
Explain 3 Tier Architecture For A Dbms Why Mapping Is Required In The following diagram shows the three level architecture of the dbms (database management system). mapping is used to make a connection between all three levels of the database. 3 tier architecture in dbms (database management system) is explained in this page along with the components, example, purpose and demerits. The 3 tier architecture is a widely used design pattern in database management systems (dbms) that enhances scalability, modularity, and maintenance. by dividing the system into three logical layers, this architecture ensures a clear separation of concerns, enabling better management and efficiency. The 3 tier architecture separates its tiers from each other based on the complexity of the users and how they use the data present in the database. it is the most widely used architecture to design a dbms.
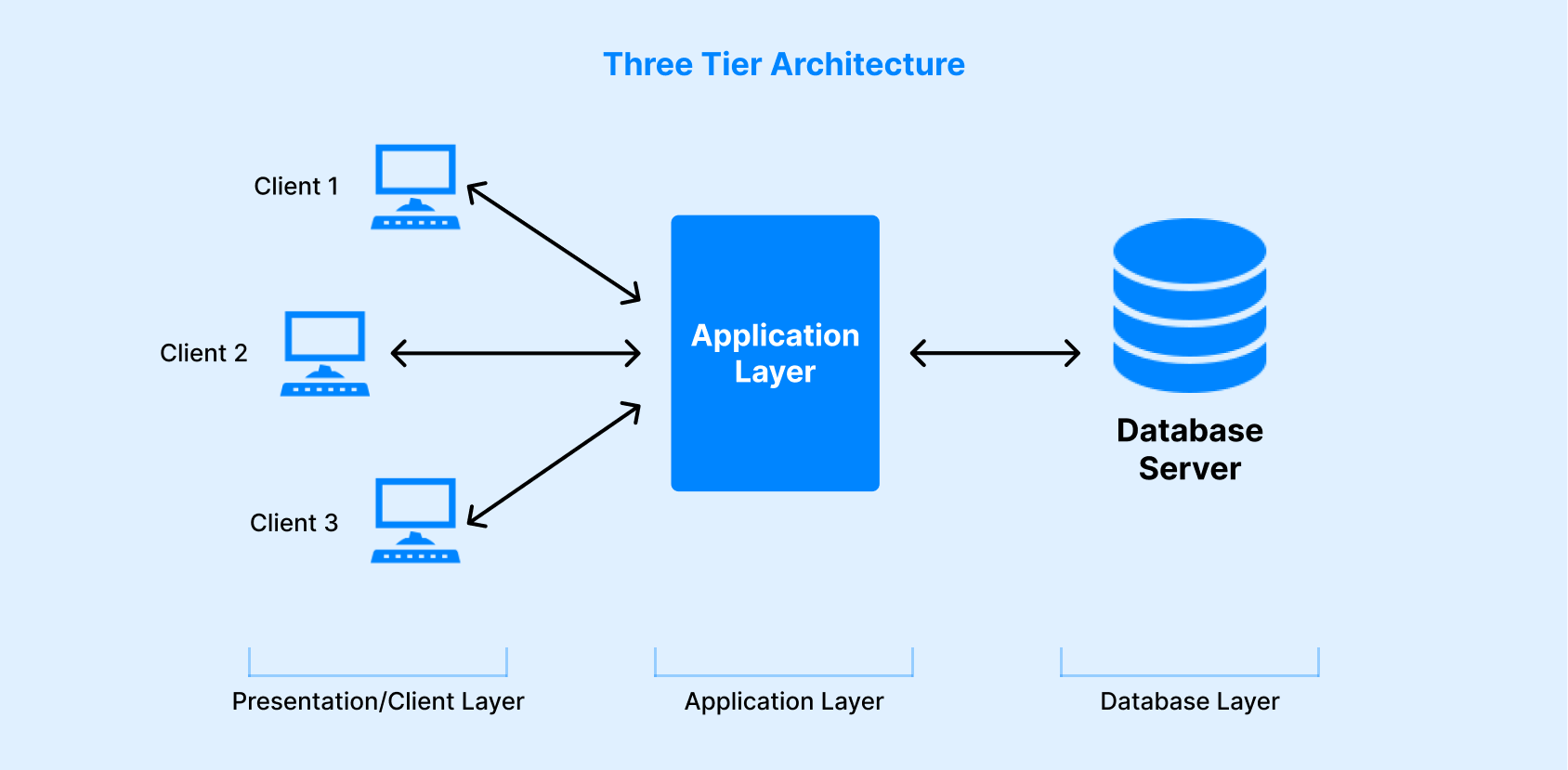
Explain 3 Tier Architecture For A Dbms Why Mapping Is Required In The 3 tier architecture is a widely used design pattern in database management systems (dbms) that enhances scalability, modularity, and maintenance. by dividing the system into three logical layers, this architecture ensures a clear separation of concerns, enabling better management and efficiency. The 3 tier architecture separates its tiers from each other based on the complexity of the users and how they use the data present in the database. it is the most widely used architecture to design a dbms.
Comments are closed.