Example Map Showing Analyte Concentration Versus Location Relative To
Example Map Showing Analyte Concentration Versus Location Relative To Download scientific diagram | example map showing analyte concentration versus location relative to breakpoint from publication: deriving background concentrations of contaminants. If we make several test mixtures that contain the analyte at various concentrations while keeping the internal standard concentration constant, we can compare the peak area ratios of the peaks in each mixture and see how they change when the concentration of the analyte changes. for example: let’s figure out the relative response.
Analyte Concentration Map Form In figure 5.2, for example, the value of ka is greatest when the analyte’s concentration is small and decreases continuously for higher concentrations of analyte. Qq plot for sulfate in a single hlu showing normal and log transformed data. brown is below breakpoint (zoomed in on lower plots); turquoise represents above breakpoint (site impacted), shown. I have been told that it is possible to estimate the concentration of a compound in a solution using the hplc peak area if you know the compound's extinction coefficient. Figure 5.4.5 : example of a normal calibration curve with a superimposed confidence interval for the analyte’s concentration. the points in blue are the original data from table 5.4.1 .

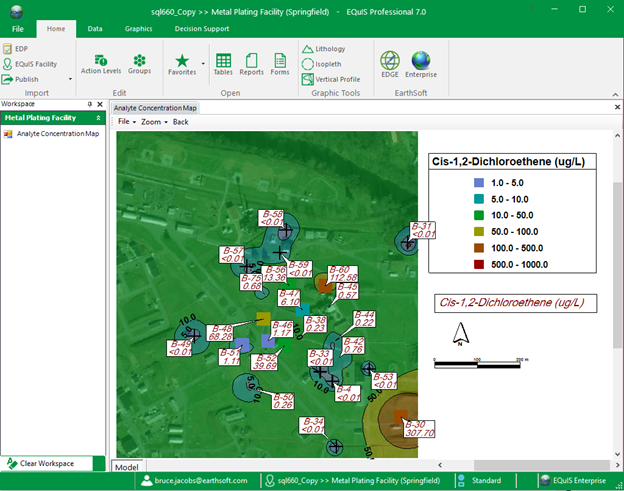
Concentration Versus Sample Volume Plot For Typical Analyte I have been told that it is possible to estimate the concentration of a compound in a solution using the hplc peak area if you know the compound's extinction coefficient. Figure 5.4.5 : example of a normal calibration curve with a superimposed confidence interval for the analyte’s concentration. the points in blue are the original data from table 5.4.1 . Description: the analyte concentration map form generates map reports of results for a single analyte featuring the elements outlined below. installation instructions: the analyte concentration map form is part of the earthsoft.forms.library.enviroinsite.dll assembly. Example: a solution containing 3.47 mm x (analyte) and 1.72 mm s (standard) gave peak areas of 3,473 and 10,222, respectively, in a chromatographic analysis. then 1.00 ml of 8.47 mm s was added to 5.00 ml of unknown x, and the mixture was diluted to 10.0 ml. Internal standards are commonly used in chromatography to calculate the concentration of an analyte. for any particular detector, the relative response factor for the analyte compared to the internal standard must be determined first. The program calculates the calibration standard istd method relative response (rr) and amount ratio (ar) for each compound at each level and stores the values in the method file:.
Comments are closed.