Double Closed Loop Feedback The Inner Loop Is Identical To The Single

Double Closed Loop Feedback The Inner Loop Is Identical To The Single The 53 bits of double s give about 16 digits of precision. the 24 bits of float s give about 7 digits of precision. From what i have read, a value of data type double has an approximate precision of 15 decimal places. however, when i use a number whose decimal representation repeats, such as 1.0 7.0, i find tha.

Solved 4 The Closed Loop Transfer Function Of A Single Loop Chegg Format %lf in printf was not supported in old (pre c99) versions of c language, which created superficial "inconsistency" between format specifiers for double in printf and scanf. Create the double[] first, add the numbers to it, and add that array to the list. (the variable should likely be declared as a list, btw, not an arraylist, unless you're specifically passing it to something that explicitly expects an arraylist.). A double typically provides 16 (±1) decimal digits. your example shows this: 4 8 12 16 v v v v 0.947368421052631578 long double 0.947368421052631526 double the answers agree to 16 digits. this is what should be expected. also, note that there's no guarantee in the c standard that a long double has more precision than a double. the last decimal digit (16th or 17th) is not necessarily accurate. When should i use double instead of decimal? has some similar and more in depth answers. using double instead of decimal for monetary applications is a micro optimization that's the simplest way i look at it.
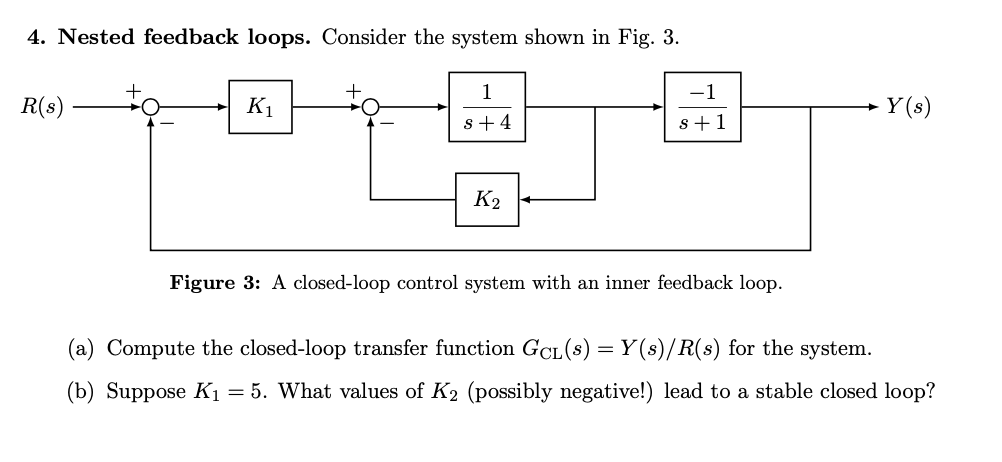
Solved Figure 3 A Closed Loop Control System With An Inner Chegg A double typically provides 16 (±1) decimal digits. your example shows this: 4 8 12 16 v v v v 0.947368421052631578 long double 0.947368421052631526 double the answers agree to 16 digits. this is what should be expected. also, note that there's no guarantee in the c standard that a long double has more precision than a double. the last decimal digit (16th or 17th) is not necessarily accurate. When should i use double instead of decimal? has some similar and more in depth answers. using double instead of decimal for monetary applications is a micro optimization that's the simplest way i look at it. Possible duplicate: long double vs double i am new to programming and i am unable to understand the difference between between long double and double in c and c . i tried to google it but was unab. Double free means free (x) was called twice in a row with the same value of x. somewhere in your code free (x) is called and then most likely in another piece of code free (x) is called again. the easiest way to isolate the problem is to use gdb and observe what is happening as you step through your code. What is the difference between decimal, float and double in ? when would someone use one of these?. Now by accessing elements c[0] through c[sizeof(double) 1] you will see the internal representation of type double. you can use bitwise operations on these unsigned char values, if you want to. note, again, that in general case in order to access internal representation of type int you have to do the same thing.

Double Closed Loop Feedback Configuration Download Scientific Diagram Possible duplicate: long double vs double i am new to programming and i am unable to understand the difference between between long double and double in c and c . i tried to google it but was unab. Double free means free (x) was called twice in a row with the same value of x. somewhere in your code free (x) is called and then most likely in another piece of code free (x) is called again. the easiest way to isolate the problem is to use gdb and observe what is happening as you step through your code. What is the difference between decimal, float and double in ? when would someone use one of these?. Now by accessing elements c[0] through c[sizeof(double) 1] you will see the internal representation of type double. you can use bitwise operations on these unsigned char values, if you want to. note, again, that in general case in order to access internal representation of type int you have to do the same thing.
Comments are closed.