Does A Large Cpu Cache Minimise The Need For Fast Ram
What S The Difference Between Ram And Cache Memory Steve and tim answer whether cpu cache can minimise the need for fast ram and they use the 5800x3d as an example here. more. When the l3 is large enough that you don't need to go to ram then the ram speed is irrelevant but l3 requirements have been going up constantly over time, by the time the x3d is on the lower end of l3 cache sizes the x3d system with the fastest ram will perform best.
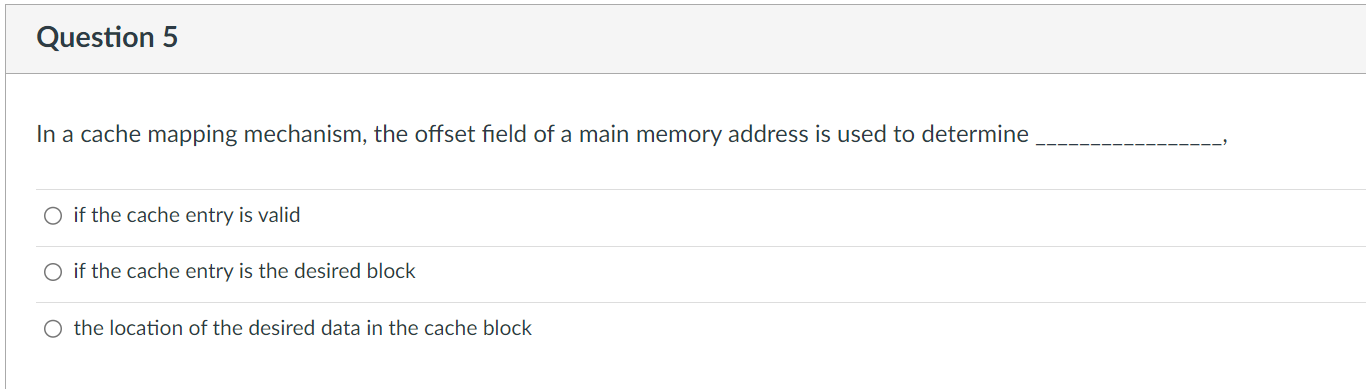
Solved Cache Memory Is Typically Positioned Between Cpu And Chegg A larger cache means that more data can be stored close to the processor, reducing the need to access slower ram. this results in faster execution of tasks, lower latency, and improved system responsiveness. So the answer to your first question is: technically (probably) possible, but unlikely to make sense, since l3 cache in modern cpus with size of just a few mbs has read latency of about dozens of cycles. performance depends more on memory access pattern than on cache size. Cpu cache memory was developed to keep up with the demands of processors when they outpaced the speed of system memory (ram) in the 1980s. today's cpus feature enormous amounts of. The primary role of cpu cache is to reduce latency when accessing frequently used data. by storing this data close to the cpu, the cache allows for quicker retrieval compared to fetching data from the slower ram.
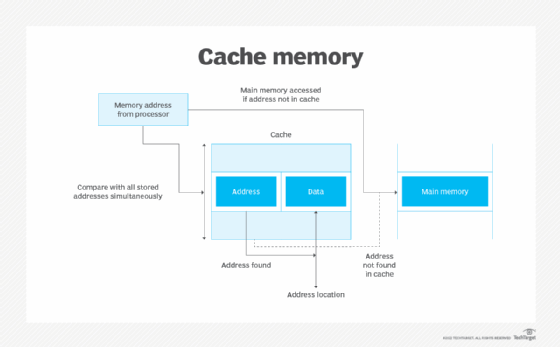
Use Ram As Cpu Cache Smartadm Ru Cpu cache memory was developed to keep up with the demands of processors when they outpaced the speed of system memory (ram) in the 1980s. today's cpus feature enormous amounts of. The primary role of cpu cache is to reduce latency when accessing frequently used data. by storing this data close to the cpu, the cache allows for quicker retrieval compared to fetching data from the slower ram. If the data is found in the cache (a cache hit), the cpu can retrieve it much faster than fetching it from ram. on the other hand, if the data is not in the cache (a cache miss), the cpu retrieves it from ram and also stores a copy in the cache for future access. In some cases you may benefit more from diverting some of your budget to faster ram than to more cache on your cpu. the most important rule is not to get bogged down in how many megabytes or levels of cache a cpu has. A computer with a larger cache is faster because it takes less time to retrieve information from its own memory than if it had to go back and fetch it from remote storage devices like hard drives and ram. A bigger cache means that the cpu will have to rely less on accessing information from ram or permanent storage (hdds and ssds), allowing it to perform at maximum capacity for longer.
Comments are closed.