Diversity Scheme In Telecommunication Assignment Point
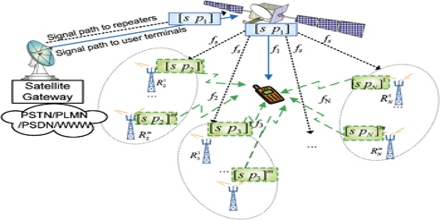
Diversity Scheme In Telecommunication Assignment Point In telecommunications, a diversity scheme describes a method intended for improving the reliability of a message signal by using two or more communication channels with different characteristics. In telecommunications, a diversity scheme refers to a method for improving the reliability of a message signal by using two or more communication channels with different characteristics.

Telecommunication Assignment Pdf Abstract this report provides a brief introduction to the various types of diversity systems in wireless systems. diversity is a powerful communication receiver technique that provides wireless link improvement at a relatively low cost. Superposition of multiple signals at the receiver causes random amplitude variation which is known as fading. a mechanism that is used to decrease the effect of fading is called diversity. it is used to compensate for fading channel impairments. One effective solution is proposed for wireless system named diversity, with out the requirement of power or extra bandwidth. this paper discusses about the characteristics of fading channels and a broad classification of various diversity techniques. Diversity schemes provide the means to generate two or more uncorrelated fading signals at the mobile reception point. the information carried by the two different received signals is the same, but the multipath fading, at any given time, is different for the two signals.

Diversity Scheme Pdf One effective solution is proposed for wireless system named diversity, with out the requirement of power or extra bandwidth. this paper discusses about the characteristics of fading channels and a broad classification of various diversity techniques. Diversity schemes provide the means to generate two or more uncorrelated fading signals at the mobile reception point. the information carried by the two different received signals is the same, but the multipath fading, at any given time, is different for the two signals. Describe the three most commonly used diversity schemes. diversity it suggests that there is more than one transmission path or method of transmission available between a transmitter and a receiver. Spatial diversity is the most widely used diversity technique. in this technique multiple antennas are strategically spaced and connected to common receiving system. while one antenna sees a signal null, one of the other antennas may see a signal peak, and the receiver is able to select the antenna with the best signal at any time. What is diversity? diversity schemes provides two or more inputs at the receiver such that the fading phenomena among these inputs are uncorrelated if one radio path undergoes deep fade at a particular point in time, another independent (or at least highly uncorrelated) path may have a strong signal at that input. Spatial diversity involves transmitting the same signal from multiple antennas but with different coding or modulation schemes, or at different times or frequencies, to combat multipath fading and improve signal robustness.

Assignment Telecom Transmission Switching Technique Pdf Describe the three most commonly used diversity schemes. diversity it suggests that there is more than one transmission path or method of transmission available between a transmitter and a receiver. Spatial diversity is the most widely used diversity technique. in this technique multiple antennas are strategically spaced and connected to common receiving system. while one antenna sees a signal null, one of the other antennas may see a signal peak, and the receiver is able to select the antenna with the best signal at any time. What is diversity? diversity schemes provides two or more inputs at the receiver such that the fading phenomena among these inputs are uncorrelated if one radio path undergoes deep fade at a particular point in time, another independent (or at least highly uncorrelated) path may have a strong signal at that input. Spatial diversity involves transmitting the same signal from multiple antennas but with different coding or modulation schemes, or at different times or frequencies, to combat multipath fading and improve signal robustness.
Comments are closed.