Discrete Fourier Transform Dft Dft Transforms The Time Domain

Download Pdf Discrete Fourier Transform Dft Ksufac Ksu Edu Sa The dft is equivalent to the dtft of a windowed version of the input signal that is then sampled and scaled in amplitude. the windowing smears the spectral representation because of discontinuities introduced by the windowing. In mathematics, the discrete time fourier transform (dtft) is a form of fourier analysis that is applicable to a sequence of discrete values. the dtft is often used to analyze samples of a continuous function.

Solved 1 3 Dft The Discrete Fourier Transform Dft Can Be Chegg Equation (67.4) is called the discrete fourier transform or dft in recognition of the fact that it is a fourier transformation, and it is discrete in both time and frequency.1 the dft takes n samples in the time domain and transforms them into n values xŒk in the frequency domain. In reality, the only member of this family that is relevant to digital signal processing is the discrete fourier transform (dft). this type of transform operates on sampled time domain signals which are periodic, as shown in figure 1 (d). How can we compute the dtft? the dtft has a big problem: it requires an in nite length summation, therefore you can't compute it on a computer. the dft solves this problem by assuming a nite length signal. Discrete fourier transform (dft) dft transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. four types of fourier transform.
Discrete Fourier Transform Dft Discrete Fourier Transform Research 1 How can we compute the dtft? the dtft has a big problem: it requires an in nite length summation, therefore you can't compute it on a computer. the dft solves this problem by assuming a nite length signal. Discrete fourier transform (dft) dft transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. four types of fourier transform. Moreover, continuous fourier transform could be evaluated for a signal that exists in a time domain from −∞ to ∞. conversely, dft is evaluated for a finite time period known as window (typically the fundamental period t) rather than an infinite time period if the waveform is periodic (lyons, 2011). Compute the dft of the signal and the magnitude and phase of the transformed sequence. decrease round off error when computing the phase by setting small magnitude transform values to zero. to plot the magnitude and phase in degrees, type the following commands:. The discrete fourier transform (dft) converts a finite sequence of equally spaced samples of a function into a sequence of equally spaced samples of the discrete time fourier transform (dtft), which is a complex valued function of frequency. The discrete fourier transform (dft) allows the computation of spectra from discrete time data. while in discrete time we can exactly calculate spectra, for analog signals no similar exact spectrum computation exists.

Discrete Fourier Transform Dft Dft Transforms The Time Domain Moreover, continuous fourier transform could be evaluated for a signal that exists in a time domain from −∞ to ∞. conversely, dft is evaluated for a finite time period known as window (typically the fundamental period t) rather than an infinite time period if the waveform is periodic (lyons, 2011). Compute the dft of the signal and the magnitude and phase of the transformed sequence. decrease round off error when computing the phase by setting small magnitude transform values to zero. to plot the magnitude and phase in degrees, type the following commands:. The discrete fourier transform (dft) converts a finite sequence of equally spaced samples of a function into a sequence of equally spaced samples of the discrete time fourier transform (dtft), which is a complex valued function of frequency. The discrete fourier transform (dft) allows the computation of spectra from discrete time data. while in discrete time we can exactly calculate spectra, for analog signals no similar exact spectrum computation exists.

Ppt Discrete Time Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform Dtft The discrete fourier transform (dft) converts a finite sequence of equally spaced samples of a function into a sequence of equally spaced samples of the discrete time fourier transform (dtft), which is a complex valued function of frequency. The discrete fourier transform (dft) allows the computation of spectra from discrete time data. while in discrete time we can exactly calculate spectra, for analog signals no similar exact spectrum computation exists.
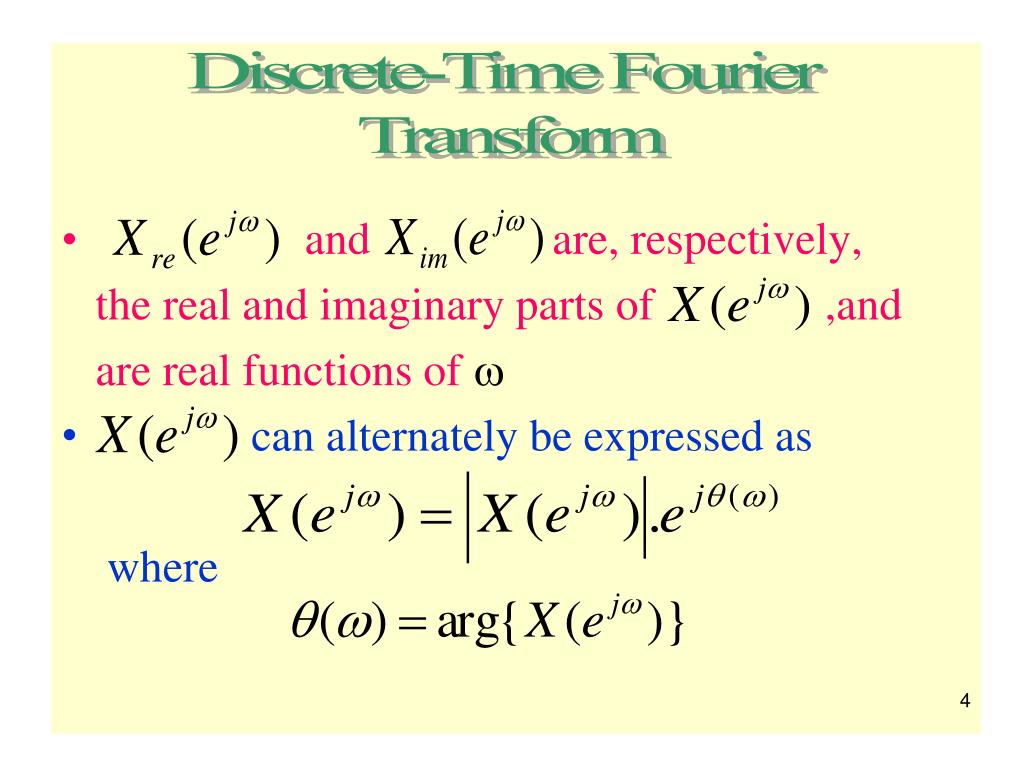
Ppt Discrete Time Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform Dtft
Comments are closed.