Diffusion Mods Explained By Stable Diffusions Creator Bjorn Ommer

177 Björn Ommer Diffusion Mods Explained By Stable Diffusion S Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. the material that diffuses could be a solid, liquid or gas. The result of diffusion is a gradual mixing of material such that the distribution of molecules is uniform. since the molecules are still in motion, but an equilibrium has been established, the result of molecular diffusion is called a "dynamic equilibrium".

Stable Diffusion Models For Image Synthesis With Conditional Priors The meaning of diffusion is the state of being spread out or transmitted especially by contact : the action of diffusing. how to use diffusion in a sentence. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread into an available area. learn about the different types of diffusion, passive, facilitated and osmosis. Diffusion can be described as the random movement of particles through space, usually due to a concentration gradient. diffusion is a spontaneous process and is a result of the random thermal motions between two particles. Diffusion describes the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. this process continues until particles are evenly distributed. for example, food coloring in water gradually spreads to tint the entire volume.

Eye On A I On Linkedin Diffusion Mods Explained By Stable Diffusion S Diffusion can be described as the random movement of particles through space, usually due to a concentration gradient. diffusion is a spontaneous process and is a result of the random thermal motions between two particles. Diffusion describes the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. this process continues until particles are evenly distributed. for example, food coloring in water gradually spreads to tint the entire volume. Diffusion is the movement of a molecule down a concentration gradient, from an area of its high concentration to an area of its low concentration. this process is passive, i.e. it requires no input of additional energy; the concentration gradient alone is enough to drive the process. Learn about the types of diffusion, including simple and facilitated diffusion, and discover the factors affecting diffusion rates. understand real life examples of diffusion, its causes, and its critical significance in biological systems, such as gas exchange and nutrient transport. Diffusion is the natural movement of particles from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration, driven by differences in concentration or energy levels. Diffusion is the process of movement of solutes and molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration across the membrane. this process is caused by the intrinsic kinetic energy of particles, resulting in random motion.
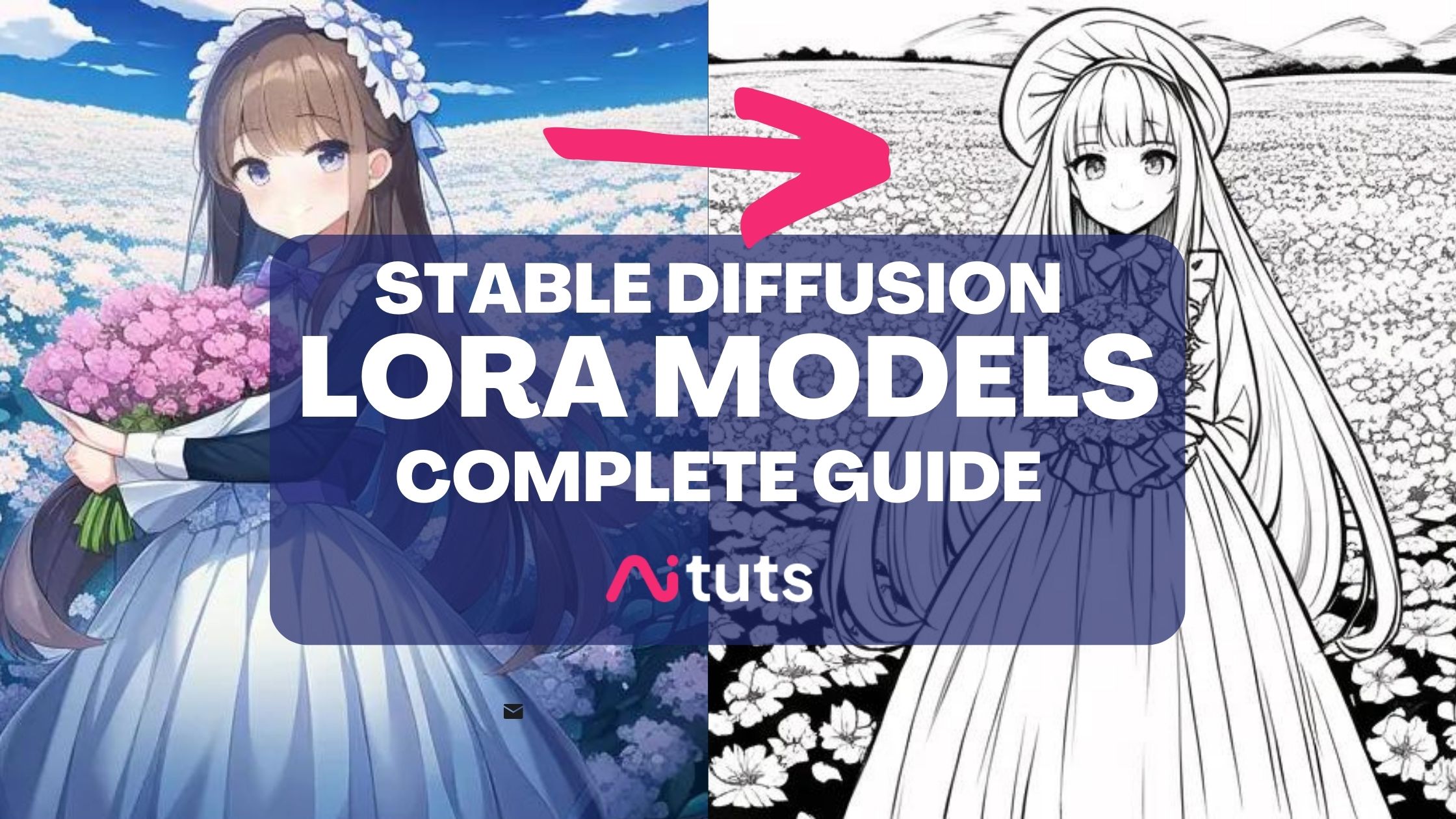
Beginner Concepts Aituts Diffusion is the movement of a molecule down a concentration gradient, from an area of its high concentration to an area of its low concentration. this process is passive, i.e. it requires no input of additional energy; the concentration gradient alone is enough to drive the process. Learn about the types of diffusion, including simple and facilitated diffusion, and discover the factors affecting diffusion rates. understand real life examples of diffusion, its causes, and its critical significance in biological systems, such as gas exchange and nutrient transport. Diffusion is the natural movement of particles from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration, driven by differences in concentration or energy levels. Diffusion is the process of movement of solutes and molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration across the membrane. this process is caused by the intrinsic kinetic energy of particles, resulting in random motion.
Comments are closed.