Differences Between Conjugated Bilirubin And Unconjugated Bilirubin Direct And Indirect Bilirubin

Solved Indirect Or Unconjugated Bilirubin Becomes Direct Or Chegg There are two forms of bilirubin: unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin and conjugated (direct) bilirubin. unconjugated bilirubin is the initial form of bilirubin produced by the breakdown of red blood cells, while conjugated bilirubin is the processed, water soluble form that is excreted from the body. Difference between conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin: understand the comparison of conjugated vs unconjugated bilirubin on the basis of meaning, functions and existence.
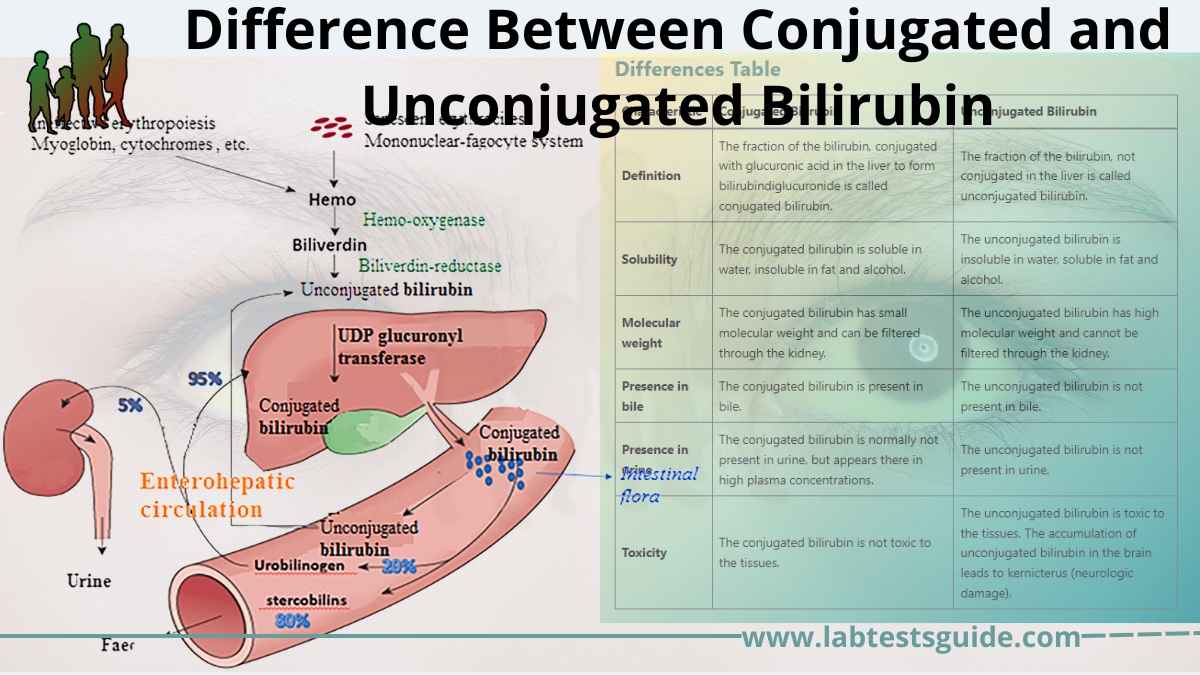
Differences Between Conjugated And Unconjugated Bilirubin Ltg Today, we are going to talk about the two different forms. so what’s the difference? in short, one is considered “normal” and shows up after a couple days of life. the other is “abnormal” and usually appears within the first few days of life. also known as “indirect” bilirubin or the “normal” type. what causes unconjugated bili to increase?. When old red cells pass through the spleen, macrophages eat them up and break down the heme into unconjugated bilirubin (which is not water soluble). the unconjugated bilirubin is then sent to the liver, which conjugates the bilirubin with glucuronic acid, making it soluble in water. Unconjugated bilirubin also known as indirect bilirubin, is a fat soluble form of bilirubin that is formed during the initial chemical breakdown of hemoglobin and while being transported in the blood, is mostly bound to albumin to the liver. Bilirubin is an orange yellow pigment that occurs normally when part of your red blood cells break down. your liver takes the bilirubin from your blood and changes its chemical makeup so that.

Differences Between Conjugated And Unconjugated Bilirubin Lab Tests Guide Unconjugated bilirubin also known as indirect bilirubin, is a fat soluble form of bilirubin that is formed during the initial chemical breakdown of hemoglobin and while being transported in the blood, is mostly bound to albumin to the liver. Bilirubin is an orange yellow pigment that occurs normally when part of your red blood cells break down. your liver takes the bilirubin from your blood and changes its chemical makeup so that. Hepatocytes transform bilirubin into a water soluble product by a process known as conjugation. conjugated bilirubin can then be excreted into bile. hyperbilirubinemia can result from either the conjugated or unconjugated fractions. the conjugated fraction reacts directly with ehrlich's diazo reagent and is thus called direct bilirubin. The conjugated bilirubin has small molecular weight and can be filtered through the kidney. the unconjugated bilirubin has high molecular weight and cannot be filtered through the kidney. the conjugated bilirubin is present in bile, while the unconjugated bilirubin is not present in bile. Learn the key differences between conjugated bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin, including their formation, significance, and clinical implications. Unconjugated bilirubin forms a waste product from haemoglobin breakdown, while conjugated bilirubin results from the liver processing unconjugated bilirubin. conjugated bilirubin is water soluble, whereas unconjugated bilirubin is not.

Differences Between Conjugated And Unconjugated Bilirubin Lab Tests Guide Hepatocytes transform bilirubin into a water soluble product by a process known as conjugation. conjugated bilirubin can then be excreted into bile. hyperbilirubinemia can result from either the conjugated or unconjugated fractions. the conjugated fraction reacts directly with ehrlich's diazo reagent and is thus called direct bilirubin. The conjugated bilirubin has small molecular weight and can be filtered through the kidney. the unconjugated bilirubin has high molecular weight and cannot be filtered through the kidney. the conjugated bilirubin is present in bile, while the unconjugated bilirubin is not present in bile. Learn the key differences between conjugated bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin, including their formation, significance, and clinical implications. Unconjugated bilirubin forms a waste product from haemoglobin breakdown, while conjugated bilirubin results from the liver processing unconjugated bilirubin. conjugated bilirubin is water soluble, whereas unconjugated bilirubin is not.

Serum Conjugated And Unconjugated Bilirubin Concentration Between Learn the key differences between conjugated bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin, including their formation, significance, and clinical implications. Unconjugated bilirubin forms a waste product from haemoglobin breakdown, while conjugated bilirubin results from the liver processing unconjugated bilirubin. conjugated bilirubin is water soluble, whereas unconjugated bilirubin is not.
Comments are closed.