Difference Between Vector And Raster Data In Gis Sheryinet

Vector Vs Raster What S The Difference Between Gis Spatial Data Types Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. The main difference between raster and vector data in gis is how they store spatial information. raster data uses pixels to represent continuous features, while vector data uses geometric shapes to represent specific locations and boundaries.

Difference Between Vector And Raster Data In Gis Sheryinet Different from vector, raster is well suited for continuous data, such as satellite images, aerial photography, and elevation models. unlike vector data, raster data allows for multiple bands, which refer to layers of data for each pixel. The two primary types of data used in gis application are vector and raster with each having distinct set of characteristic and applications. in this blog, our experts will provide you a quick peep into the gis data types, differences, and advantages. Let’s dive into the key differences between raster and vector data, explore their pros and cons, and see how they are used in real world applications — visually explained for better. In gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. understanding the differences between these data types and when to use them is essential for effective gis analysis.
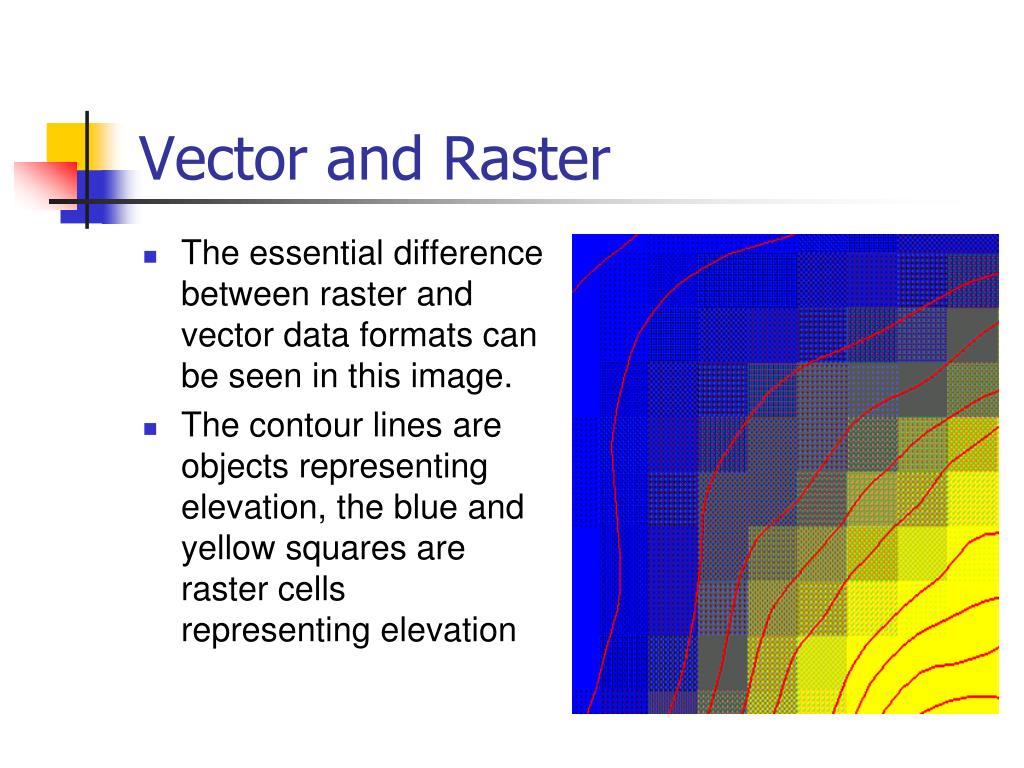
Difference Between Vector And Raster Data In Gis Sheryinet Let’s dive into the key differences between raster and vector data, explore their pros and cons, and see how they are used in real world applications — visually explained for better. In gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. understanding the differences between these data types and when to use them is essential for effective gis analysis. Two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. in this article, we will discuss the basics of these data models, their differences, and how they are used in gis. These numerical values can be used to translate map information into digital form, in both vector and raster formats. what is raster data? raster data is like a digital photograph. the entire area of the map is subdivided into a grid of tiny cells, or pixels. Discover the key differences between vector and raster mapping formats, from data storage and visualization to accuracy and cost considerations in gis applications. Rasters capture continuous data, while vectors represent discrete data. points represent individual locations on the earth's surface. each point is defined by its coordinates, typically as latitude and longitude. points are used to mark specific landmarks or points of interest.

Difference Between Vector And Raster Data In Gis Grosfinancial 4030 Two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. in this article, we will discuss the basics of these data models, their differences, and how they are used in gis. These numerical values can be used to translate map information into digital form, in both vector and raster formats. what is raster data? raster data is like a digital photograph. the entire area of the map is subdivided into a grid of tiny cells, or pixels. Discover the key differences between vector and raster mapping formats, from data storage and visualization to accuracy and cost considerations in gis applications. Rasters capture continuous data, while vectors represent discrete data. points represent individual locations on the earth's surface. each point is defined by its coordinates, typically as latitude and longitude. points are used to mark specific landmarks or points of interest.
Comments are closed.