Difference Between Coroutinescope And Coroutinescope In Kotlin Delft
Difference Between Coroutinescope And Coroutinescope In Kotlin Delft Coroutinescope() is nothing but a factory of coroutinescope objects, and a coroutinescope object is nothing but a holder of a coroutinecontext. it has no active role in coroutines, but it's an important part of the infrastructure that makes it easy to do structured concurrency properly. This blog will explore the differences between globalscope and coroutinescope, their use cases, and practical examples to help you choose the right one for your kotlin projects.
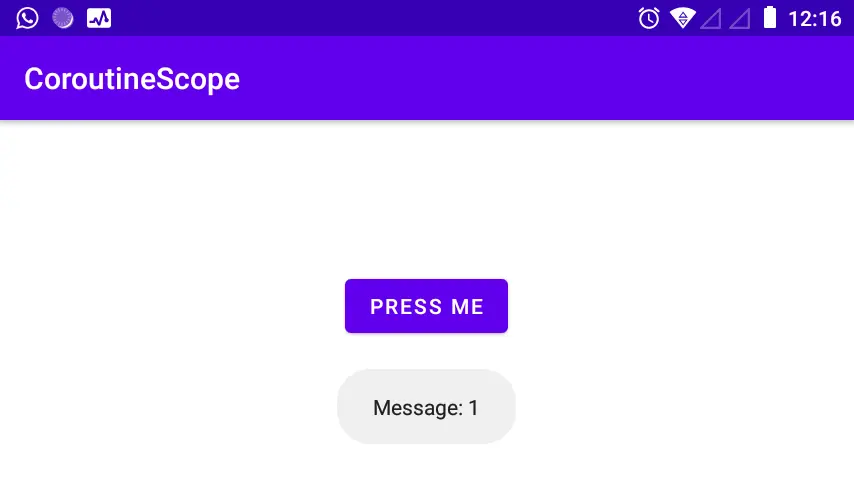
Difference Between Coroutinescope And Coroutinescope In Kotlin Delft Every coroutine builder (like launch, async, etc.) is an extension on coroutinescope and inherits its coroutinecontext to automatically propagate all its elements and cancellation. Can anyone give clarity between functions coroutinescope() and coroutinescope()? when i tried to check in source, i found that both of them are functions of coroutinescope.kt. additionally, coroutinescope() is suspend function while other one is normal function. below is documentation i could find :. In order to run a coroutine we need to run it in a scope called coroutinescope. this coroutinescope help us to track running coroutine, cancel the unused coroutine to avoid memory leak. there are several scope other than coroutinescope that we want to talk about. Structured concurrency in kotlin relies heavily on coroutinescope and supervisorscope to manage coroutine lifecycles. let’s break down how they work internally and when to use each.
Difference Between Coroutinescope And Coroutinescope In Kotlin Delft In order to run a coroutine we need to run it in a scope called coroutinescope. this coroutinescope help us to track running coroutine, cancel the unused coroutine to avoid memory leak. there are several scope other than coroutinescope that we want to talk about. Structured concurrency in kotlin relies heavily on coroutinescope and supervisorscope to manage coroutine lifecycles. let’s break down how they work internally and when to use each. In this article, we'll explore the main types of scopes in kotlin and their differences. you'll see how choosing the right scope can simplify managing coroutines in your code. It's not just boilerplate. the behavior will be different if you pass a coroutinescope other than the current coroutine's scope (it won't cause the top level coroutine to throw if the coroutine in some other scope throws). also, coroutinescope returns a result and launch doesn't. Is there difference between these two, which way is preferred? yes, there's a fundamental difference that makes one correct and the other incorrect. You might say that coroutinescope formalizes the way the coroutinecontext is inherited. coroutinescope has no data on its own, it just holds a coroutinecontext.
Comments are closed.