Cumulative Distribution Functions And Probability Density Functions
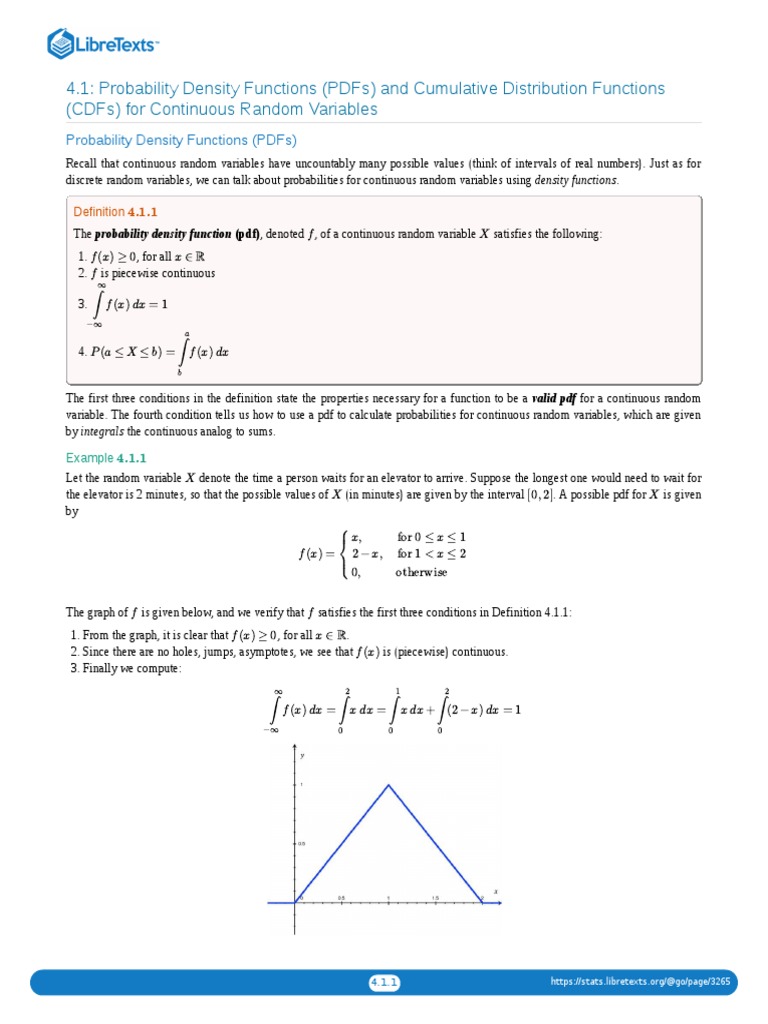
4 1 Probability Density Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Distribution Recall that continuous random variables have uncountably many possible values (think of intervals of real numbers). just as for discrete random variables, we can talk about probabilities for continuous random variables using density functions. Both probability density functions (pdfs) and cumulative distribution functions provide likelihoods for random variables. however, pdfs calculate probability densities for x, while cdfs give the chances for ≤ x.
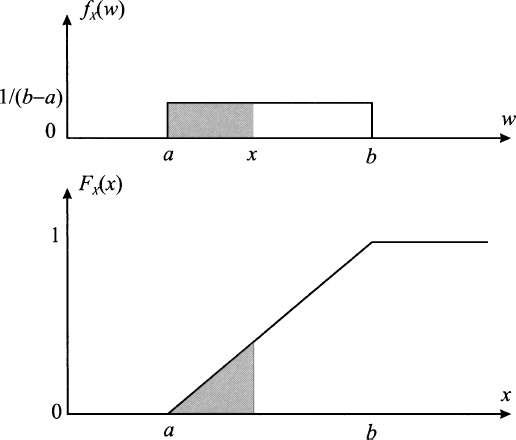
Cumulative Distribution And Probability Density Functions My Blog In today's article, we will delve into the fascinating world of cumulative distribution functions (cdfs) and probability density functions (pdfs). understanding these fundamental concepts is essential for anyone looking to gain a deeper insight into probability and statistics. While the cdf provides the cumulative probability of observing values less than or equal to a certain value, the pdf gives the probability density at specific points. understanding the differences and similarities between these two functions is crucial for effectively interpreting and analyzing data in statistical analysis. Let’s dive into the connection between the probability density function (pdf) and the cumulative distribution function (cdf). one of the key relationships is that the cdf is the. Any probability density function integrates to so the probability density function of the continuous uniform distribution is graphically portrayed as a rectangle where is the base length and is the height.

A Probability Density Functions B Cumulative Distribution Let’s dive into the connection between the probability density function (pdf) and the cumulative distribution function (cdf). one of the key relationships is that the cdf is the. Any probability density function integrates to so the probability density function of the continuous uniform distribution is graphically portrayed as a rectangle where is the base length and is the height. This article will discuss the definitions of cumulative distribution function (cdf) vs probability density function (pdf) and their unique roles and interactions. Double gaussian (two piece normal) distribution. 1 . 11. inverse gaussian distribution. 2 r ! (x) is the c.d.f. of standard normal distribution. 12. laplace distribution. 13. beta laplace distribution. 14. double exponential (skew laplace) distribution. 1 > 0 and 2 > 0. 15. asymmetric laplace distribution. is an asymmetry parameter. 16. When working with probability distributions, two key concepts that frequently come up are the probability density function (pdf) and the cumulative distribution function (cdf). these functions describe how probabilities are distributed over a range of values for a random variable.

Cumulative Distribution Functions Probability Density Functions And This article will discuss the definitions of cumulative distribution function (cdf) vs probability density function (pdf) and their unique roles and interactions. Double gaussian (two piece normal) distribution. 1 . 11. inverse gaussian distribution. 2 r ! (x) is the c.d.f. of standard normal distribution. 12. laplace distribution. 13. beta laplace distribution. 14. double exponential (skew laplace) distribution. 1 > 0 and 2 > 0. 15. asymmetric laplace distribution. is an asymmetry parameter. 16. When working with probability distributions, two key concepts that frequently come up are the probability density function (pdf) and the cumulative distribution function (cdf). these functions describe how probabilities are distributed over a range of values for a random variable.

Probability Distribution Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Density When working with probability distributions, two key concepts that frequently come up are the probability density function (pdf) and the cumulative distribution function (cdf). these functions describe how probabilities are distributed over a range of values for a random variable.
Comments are closed.