Constructivism Learning And Teaching
Constructivism Learning Theory 41 Off Pinnaxis Constructivism in the philosophy of education is the belief that learners actively construct their own knowledge and understanding of the world through their experiences, interactions, and reflections. Constructivism in education is a theory that suggests that learners do not passively acquire knowledge through direct instruction. instead, they construct their understanding through experiences and social interaction, integrating new information with their existing knowledge.

Constructivism Theory For Teaching And Learning Learning Performance The idea that students actively construct knowledge is central to constructivism. students add (or build) their new experiences on top of their current foundation of understanding. Constructivism is an action oriented approach to learning, requiring students to build upon existing knowledge to understand better and apply new concepts. teachers are there to shepherd students through their cognitive processing and devise classroom activities to help students learn. Constructivism is an important learning theory that educators use to help their students learn. constructivism is based on the idea that people actively construct or make their own knowledge, and that reality is determined by your experiences as a learner. Constructivism learning theory holds that learners construct knowledge as they reflect on and interpret their own experiences. the influence of constructivism is seen in educational practices and policies today throughout primary and secondary education.

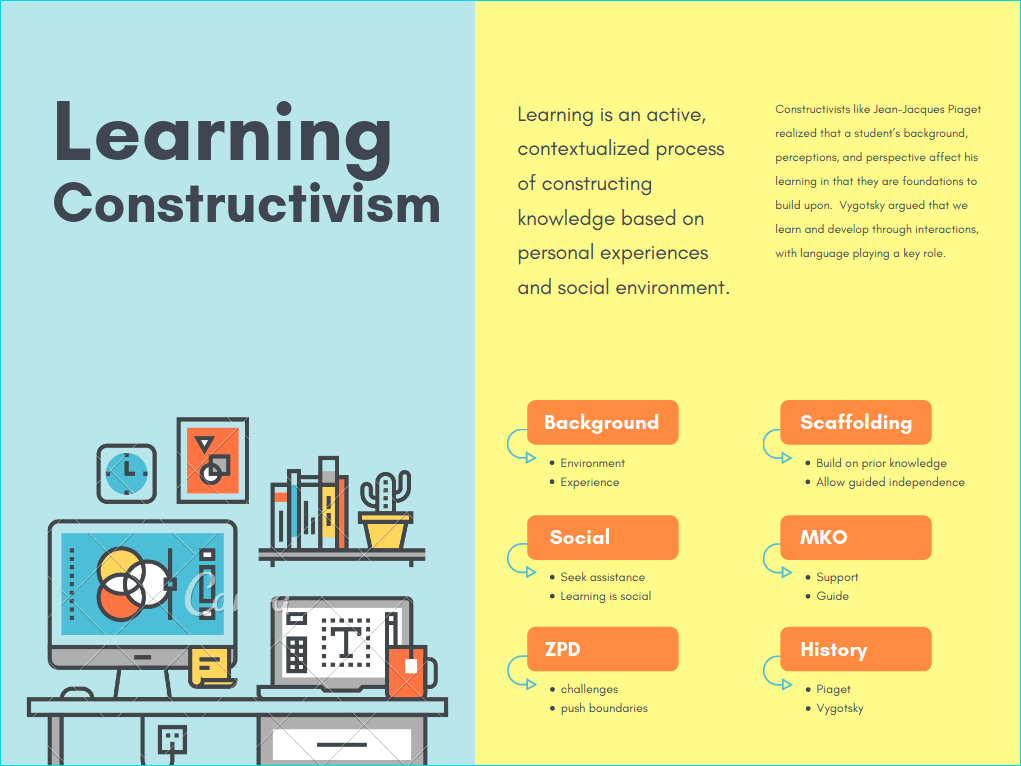
Constructivist Learning Theory Elm Learning Constructivism is an important learning theory that educators use to help their students learn. constructivism is based on the idea that people actively construct or make their own knowledge, and that reality is determined by your experiences as a learner. Constructivism learning theory holds that learners construct knowledge as they reflect on and interpret their own experiences. the influence of constructivism is seen in educational practices and policies today throughout primary and secondary education. Constructivism is defined as a philosophical branch of psychology that posits that individuals construct their own understanding and knowledge through experiences and social interactions, with an emphasis on the active role of students in the learning process. Constructivism is the general methodological position that ideas are built by arranging cognitive building blocks. formed by experience and social interaction, these building blocks make up ideas, concepts and our understanding of the world. A reaction to didactic approaches such as behaviorism and programmed instruction, constructivism states that learning is an active, contextualized process of constructing knowledge rather than acquiring it. knowledge is constructed based on personal experiences and hypotheses of the environment. In constructivist classrooms, students engage in inquiry, dialogue, and real world problem solving to construct their own knowledge. contrary to common assumptions, constructivism is relevant at all levels of learning and remains a powerful guide for classroom practice.

Constructivism As A Teaching And Learning Theory By Nihad Shaikhah On Prezi Constructivism is defined as a philosophical branch of psychology that posits that individuals construct their own understanding and knowledge through experiences and social interactions, with an emphasis on the active role of students in the learning process. Constructivism is the general methodological position that ideas are built by arranging cognitive building blocks. formed by experience and social interaction, these building blocks make up ideas, concepts and our understanding of the world. A reaction to didactic approaches such as behaviorism and programmed instruction, constructivism states that learning is an active, contextualized process of constructing knowledge rather than acquiring it. knowledge is constructed based on personal experiences and hypotheses of the environment. In constructivist classrooms, students engage in inquiry, dialogue, and real world problem solving to construct their own knowledge. contrary to common assumptions, constructivism is relevant at all levels of learning and remains a powerful guide for classroom practice.
Comments are closed.