Conjugated Bilirubin Vs Unconjugated Bilirubin Lab Tests Guide
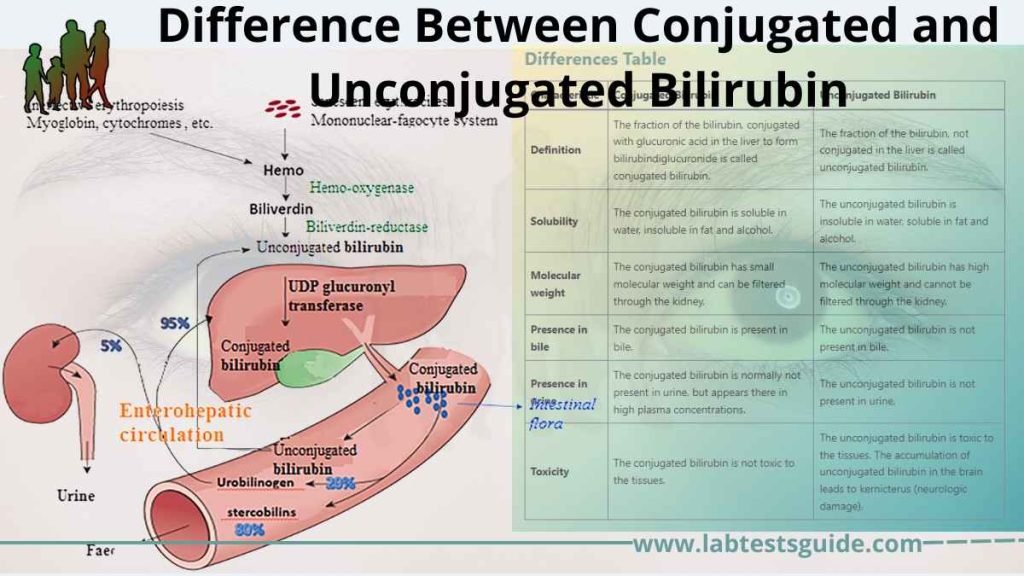
Conjugated Bilirubin Vs Unconjugated Bilirubin Lab Tests Guide There are two forms of bilirubin: unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin and conjugated (direct) bilirubin. unconjugated bilirubin is the initial form of bilirubin produced by the breakdown of red blood cells, while conjugated bilirubin is the processed, water soluble form that is excreted from the body. The unconjugated bilirubin is then sent to the liver, which conjugates the bilirubin with glucuronic acid, making it soluble in water. most of this conjugated bilirubin goes into the bile and out into the small intestine.

Conjugated Bilirubin Vs Unconjugated Bilirubin Lab Tests Guide Investigations and analysis of conjugated bilirubin, unconjugated bilirubin, urobilinogen and bilirubinuria. Also known as “indirect” bilirubin or the “normal” type. this type is unable to be conjugated by the liver and re enters enterohepatic circulation in two different ways:. It is an important marker for liver function and is commonly measured in blood tests. bilirubin exists in two forms: conjugated bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin. in this article, we will explore the attributes of both forms and understand their significance in health and disease. Unconjugated bilirubin is fat soluble however conjugated bilirubin is water soluble and hence can be excreted through kidneys. an increase in the level of conjugated bilirubin means an indication towards hepatobiliary disease.

Conjugated Bilirubin Vs Unconjugated Bilirubin Lab Tests Guide It is an important marker for liver function and is commonly measured in blood tests. bilirubin exists in two forms: conjugated bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin. in this article, we will explore the attributes of both forms and understand their significance in health and disease. Unconjugated bilirubin is fat soluble however conjugated bilirubin is water soluble and hence can be excreted through kidneys. an increase in the level of conjugated bilirubin means an indication towards hepatobiliary disease. Conjugated and unconjugated levels usually parallel each other, except in the rare complication of aplastic anemia when unconjugated bilirubin prevails. In the clinical laboratory, conjugated bilirubin is measured as direct bilirubin. if we take the total bilirubin and subtract the direct bilirubin, it provides the concentration of unconjugated bilirubin (also referred to as indirect bilirubin). The b c ratio (bilirubin conjugated unconjugated, or direct indirect bilirubin) is a measurement from a liver function panel. this ratio helps healthcare providers assess liver health and how effectively the liver processes and eliminates waste products. Unconjugated bilirubin is also called indirect bilirubin. higher than normal levels of bilirubin may indicate different types of liver problems. occasionally, higher bilirubin levels may indicate an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis).
Comments are closed.