Compact Bone Under Microscope Labeled

Compact Bone Under Microscope Labeled Compact bone is dense and composed of osteons, while spongy bone is less dense and made up of trabeculae. blood vessels and nerves enter the bone through the nutrient foramina to nourish and innervate bones. Compact bone forms the surface of all bones. the bone of the shaft of a long bone is a thick layer of compact bone. the outlined area is a cross section of an osteon of compact bone. in three dimensions an osteon is cylindrical in shape.
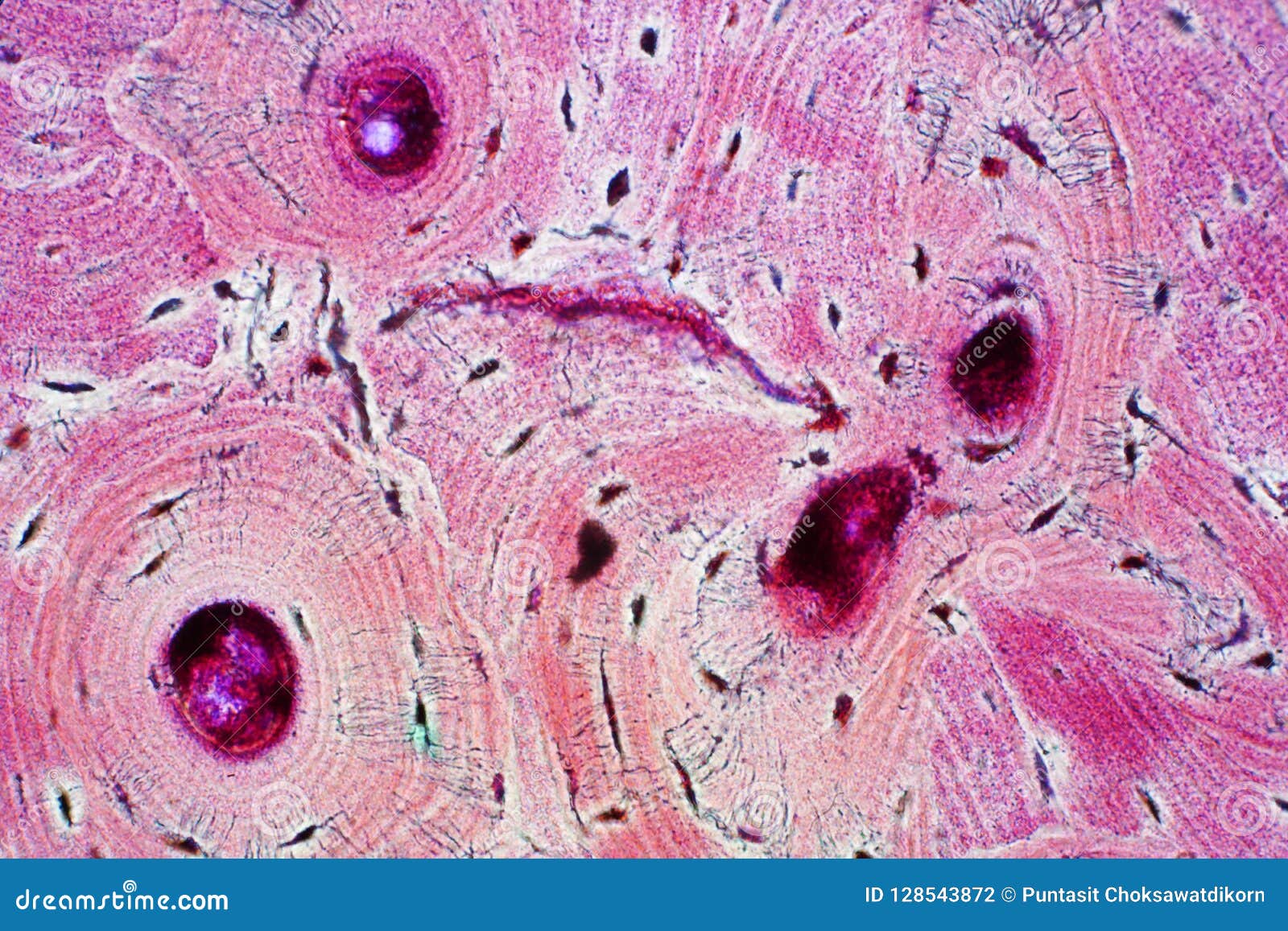
Compact Bone Under Microscope Labeled Compare and contrast the structure, function, and location of compact and spongy bone. identify the structures of an osteon from an image, model, or microscope slide. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like central haversian canal, osteon, circumferential lamallae and more. In bone, you will find two types of substances – compact and spongy substances. in this short article, i am going to describe compact bone histology with a labelled diagram. Each osteon consists of a lamellae of compact bone tissue that surround a central canal (haversian canal). the haversian canal contains the bone’s blood supplies. the boundary of an osteon is called the cement line. osteons can be arranged into woven bone or lamellar bone.

Compact Bone Structure Under Microscope Stock Photo Edit Now 1632109486 In bone, you will find two types of substances – compact and spongy substances. in this short article, i am going to describe compact bone histology with a labelled diagram. Each osteon consists of a lamellae of compact bone tissue that surround a central canal (haversian canal). the haversian canal contains the bone’s blood supplies. the boundary of an osteon is called the cement line. osteons can be arranged into woven bone or lamellar bone. (a) this cross sectional view of compact bone shows the basic structural unit, the osteon. (b) in this micrograph of the osteon, you can clearly see the concentric lamellae and central canals. Study the diagram and image below and then examine the two samples of compact, lamellar bone on this slide. this tissue was not decalcified; it was prepared using a grinding stone rather than a microtome. A three dimensional view of compact and spongy bone is seen in em 215 tibia by scanning electron microscopy. This medical image offers a detailed cross sectional view (a) of compact bone, highlighting the osteon as its basic unit, alongside a micrograph (b) that reveals the concentric lamellae and central canals at a magnified level.

Bone Under Microscope Labeled (a) this cross sectional view of compact bone shows the basic structural unit, the osteon. (b) in this micrograph of the osteon, you can clearly see the concentric lamellae and central canals. Study the diagram and image below and then examine the two samples of compact, lamellar bone on this slide. this tissue was not decalcified; it was prepared using a grinding stone rather than a microtome. A three dimensional view of compact and spongy bone is seen in em 215 tibia by scanning electron microscopy. This medical image offers a detailed cross sectional view (a) of compact bone, highlighting the osteon as its basic unit, alongside a micrograph (b) that reveals the concentric lamellae and central canals at a magnified level. Start studying microscopic labeling of compact bone. learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Explore the intricate architecture of bone tissue. this guide offers a comprehensive, identifiable breakdown of its fundamental components and dynamic nature. Observe the bone slide under the microscope. remember to follow the microscopy procedure outlined in the microscopy lab! use figure 5.2.1 5.2. 1 as a guide for what you are looking for on the slide. please focus the blood slide to 100x total magnification and take the image of the slide at 100x*. Compact bone, or cortical bone, forms the dense outer layer of long bones, providing strength and protection. it is composed of tightly packed osteons, making it ideal for supporting weight and resisting bending forces.

Bone Under Microscope Labeled A three dimensional view of compact and spongy bone is seen in em 215 tibia by scanning electron microscopy. This medical image offers a detailed cross sectional view (a) of compact bone, highlighting the osteon as its basic unit, alongside a micrograph (b) that reveals the concentric lamellae and central canals at a magnified level. Start studying microscopic labeling of compact bone. learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Explore the intricate architecture of bone tissue. this guide offers a comprehensive, identifiable breakdown of its fundamental components and dynamic nature. Observe the bone slide under the microscope. remember to follow the microscopy procedure outlined in the microscopy lab! use figure 5.2.1 5.2. 1 as a guide for what you are looking for on the slide. please focus the blood slide to 100x total magnification and take the image of the slide at 100x*. Compact bone, or cortical bone, forms the dense outer layer of long bones, providing strength and protection. it is composed of tightly packed osteons, making it ideal for supporting weight and resisting bending forces. The outermost and innermost layers of cortical bone contain no haversian canals, and the lamellae are arranged parallel with the periosteal and endosteal surfaces to form the so called. One way to classify bone tissue is based on their microscopic structure. bone tissue with a tightly packed microstructure arranged into rings is called compact bone (also called cortical or lamellar bone). compact bone structure gives bones their stiffness. Explore the unseen architecture of bone tissue. gain essential insights into its complex composition and critical role in health. Examine each bone listed below and discuss with your group which shape classification is appropriate for each. you may need to refer your textbook and or laboratory manual for help identifying each bone.
Comments are closed.