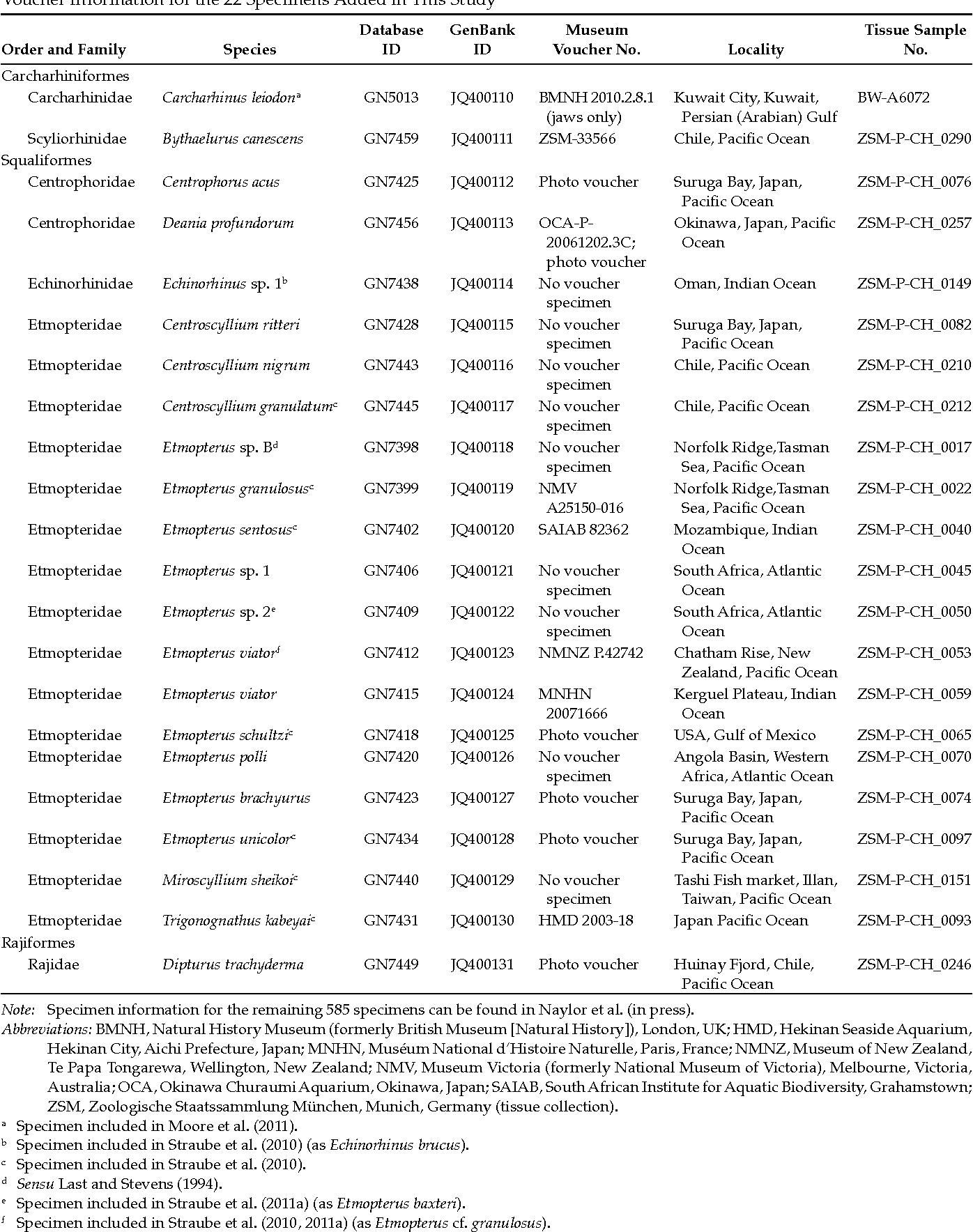
Bayesian Inference Phylogeny Based On The D1 D2 Large Subunit Rdna

Bayesian Inference Phylogeny Based On The D1 D2 Large Subunit Rdna Here we reconstructed the phylogeny of the majority of described anamorphic and teleomorphic tremellomycetous yeasts using bayesian inference, maximum likelihood, and neighbour joining analyses based on the sequences of seven genes, including three rrna genes, namely the small subunit of the ribosomal dna (rdna), d1 d2 domains of the large. Download scientific diagram | bayesian inference phylogeny based on the d1 d2 large subunit rdna region of representative yeast haplotypes from cultures isolated from.

Bayesian Inference Phylogeny Based On The D1 D2 Large Subunit Rdna Bayesian and maximum parsimony phylogenetic analyses of 92 collections of the genera basidiophora, bremia, paraperonospora, phytophthora and plasmopara were performed using nuclear large subunit ribosomal dna sequences containing the d1 and d2 regions. The results of the bayesian analysis of a phylogeny are directly correlated to the model of evolution chosen so it is important to choose a model that fits the observed data, otherwise inferences in the phylogeny will be erroneous. Here we describe bayesian inference of phylogeny and illustrate applications for inferring large trees, detecting natural selection, and choosing among models of dna substitution. A phylogenetic relationship of dinoflagellate species inferred from partial large subunit rdna sequences, including d2 to d4 and their flanking core regions, and using a consensus ml analysis, computed with mrbayes version 3.1.2.

Phylogenetic Tree From Bayesian Inference Based On Partial Large Here we describe bayesian inference of phylogeny and illustrate applications for inferring large trees, detecting natural selection, and choosing among models of dna substitution. A phylogenetic relationship of dinoflagellate species inferred from partial large subunit rdna sequences, including d2 to d4 and their flanking core regions, and using a consensus ml analysis, computed with mrbayes version 3.1.2. Sequence data from nuclear large subunit ribosomal dna was used to infer phylogenetic relationships of selected genera of the uredinales. The molecular systematics of 337 strains of basidiomycetous yeasts and yeast like fungi, representing 230 species in 18 anamorphic and 24 teleomorphic genera, was determined by sequence analysis of the d1 d2 region of the large subunit rdna. Sequence data of 26s rdna d1 d2 domains were analyzed using several procedures, including the bayesian markov chain monte carlo method of phylogenetic inference. Download scientific diagram | phylogenetic trees inferred from d1 d2 domain of 28s rdna (a) and internal ribosomal spacers its1 5.8s its2 (b) based on maximum likelihood (ml).
Bayesian Inference In Phylogeny Semantic Scholar Sequence data from nuclear large subunit ribosomal dna was used to infer phylogenetic relationships of selected genera of the uredinales. The molecular systematics of 337 strains of basidiomycetous yeasts and yeast like fungi, representing 230 species in 18 anamorphic and 24 teleomorphic genera, was determined by sequence analysis of the d1 d2 region of the large subunit rdna. Sequence data of 26s rdna d1 d2 domains were analyzed using several procedures, including the bayesian markov chain monte carlo method of phylogenetic inference. Download scientific diagram | phylogenetic trees inferred from d1 d2 domain of 28s rdna (a) and internal ribosomal spacers its1 5.8s its2 (b) based on maximum likelihood (ml).
Comments are closed.