Advantages Of Tuples Over Lists In Python

Advantages Of Tuples Over Lists In Python Lists are mutable, allowing you to modify their content, while tuples are immutable, meaning you can’t change them after creation. you should prefer tuples when you need an immutable sequence, such as function return values or constant data. In python, both tuples and lists are used for storing collections of items. however, tuples and lists serve different purposes and offer distinct advantages. this technical article.

Lists And Tuples In Python Real Python Tuples are also more memory efficient than the lists. when it comes to time efficiency, tuples have a slight advantage over lists especially when we consider lookup value. if you have data that shouldn’t change, you should choose tuple data type over lists. Learn how tuples and lists are similar and different in python, and when to use each one. tuples are immutable, hashable, and efficient for storing data, while lists are mutable, dynamic, and versatile. Understand tuples in python, their usage, benefits, and differences from lists. learn how to create, manipulate, and access elements in tuples. In my previous blogs, i have been talking about python lists, how lists are like flexible grocery bags — you can toss things in, take things out, and rearrange stuff however you like. but today, let’s understand tuples. also stick till the end, i’ve got some helpful resources at the end. let’s jump in. so… what is a tuple in python?.
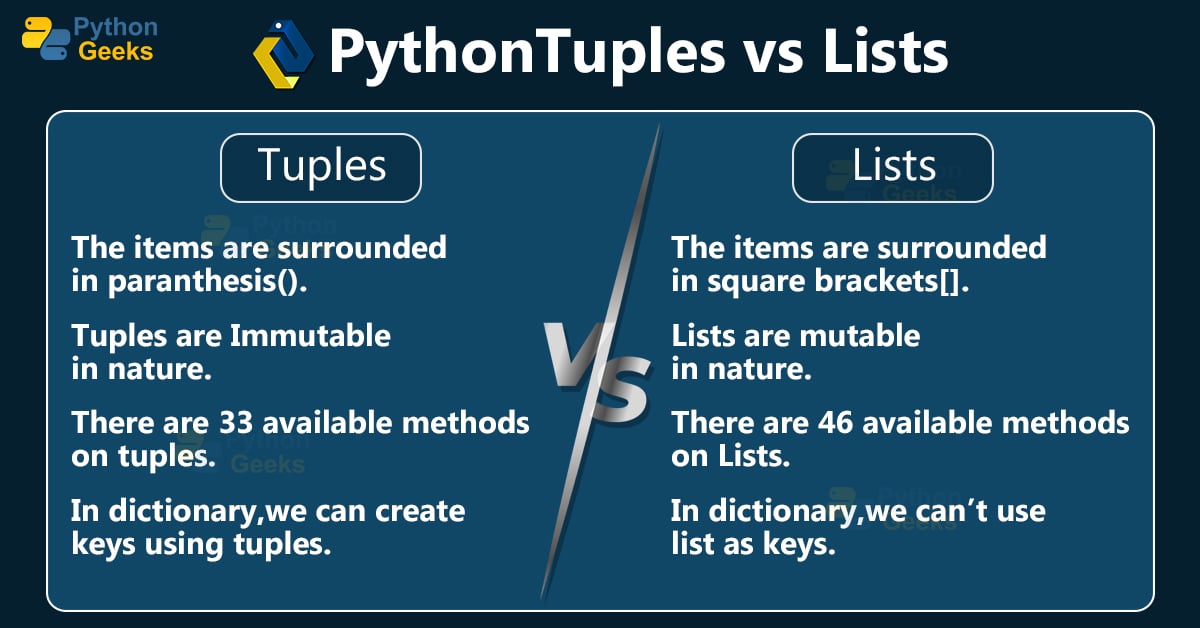
Difference Between Tuple And List In Python Tuples Vs Lists Python Understand tuples in python, their usage, benefits, and differences from lists. learn how to create, manipulate, and access elements in tuples. In my previous blogs, i have been talking about python lists, how lists are like flexible grocery bags — you can toss things in, take things out, and rearrange stuff however you like. but today, let’s understand tuples. also stick till the end, i’ve got some helpful resources at the end. let’s jump in. so… what is a tuple in python?. We’ll unravel the mysteries of why and when to use tuples over lists, giving you practical insights to optimize your code. stick with me, and i’ll show you how tuples can be a game changer in your python endeavors. When working with data structures in python, you’ll often come across lists and tuples. both are fundamental and widely used, but they serve different purposes. while lists are dynamic and versatile, tuples are immutable and efficient. Python includes built in data structures for effectively storing and manipulating sequential data. the two most general purpose options include: lists: dynamic arrays that support mutable sequences of objects. tuples: immutable sequences structurally similar to lists.

Python Tuples Vs Lists The Clash Of Mutables And Immutables Techvidvan We’ll unravel the mysteries of why and when to use tuples over lists, giving you practical insights to optimize your code. stick with me, and i’ll show you how tuples can be a game changer in your python endeavors. When working with data structures in python, you’ll often come across lists and tuples. both are fundamental and widely used, but they serve different purposes. while lists are dynamic and versatile, tuples are immutable and efficient. Python includes built in data structures for effectively storing and manipulating sequential data. the two most general purpose options include: lists: dynamic arrays that support mutable sequences of objects. tuples: immutable sequences structurally similar to lists.

Understanding Tuples In Python Python For Beginners 18 Lists And Python includes built in data structures for effectively storing and manipulating sequential data. the two most general purpose options include: lists: dynamic arrays that support mutable sequences of objects. tuples: immutable sequences structurally similar to lists.
Comments are closed.