A Detector Measures The Count Rate From A Sample Of A Radioactive

A Detector Measures The Count Rate From A Sample Of A Radioactive A detector measures the count rate from a sample of a radioactive nuclide. the graph shows the variation with time of the count rate.the nuclide has a half l. A detector measures the count rate from a sample of a radioactive nuclide. the graph shows the variation with time of the count rate. the nuclide has a half life of 20 s. the average background count rate is constant. what is the average background count rate? a. 1 s −1 b. 2 s −1 c. 3 s −1 d. 4 s −1.

Radioactive Count Rate Sciencescope To calculate the uncertainty for a count and count rate. to review the statistics for a single count (rate) versus those for a series of counts of the same sample. it is impossible to directly measure radiation in every situation at every point in space and time. Not only is there constant change in the activity of a specific sample due to the half life of the radionuclide, but there is also a fluctuation in the decay rate of a particular sample from one instant to the next due to the random nature of radioactive decay. Assuming that the background radiation has already been taken into account, calculate the half life of the source. the count rate has decreased by a factor of 1600 100 = 16. 😉 want a more accurate answer? get step by step solutions within seconds. Detector counting efficiency the detector counting efficiency (de) relates the amount of radiation emitted by a radioactive source to the amount measured in the detector.
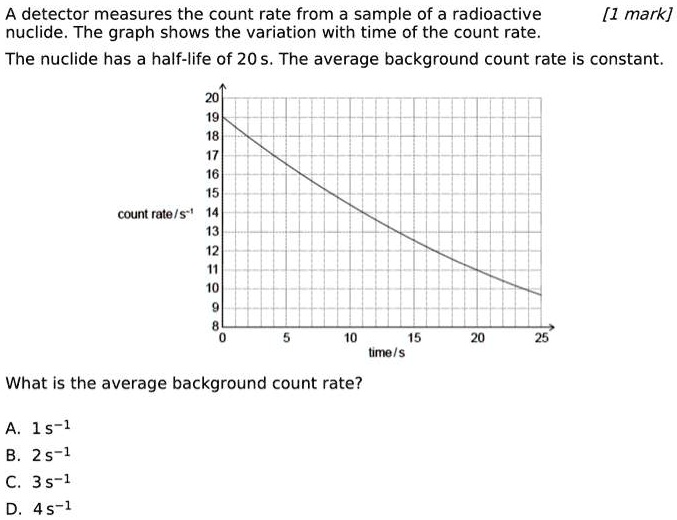
A Detector Measures The Count Rate From A Sample Of A Radioactive Assuming that the background radiation has already been taken into account, calculate the half life of the source. the count rate has decreased by a factor of 1600 100 = 16. 😉 want a more accurate answer? get step by step solutions within seconds. Detector counting efficiency the detector counting efficiency (de) relates the amount of radiation emitted by a radioactive source to the amount measured in the detector. Not the question you're searching for? a detector measures the count rate from a sample of a radioactive nuclide. the graph shows the variation with time of the count rate. the nuclide has a half life of 20 s. Geiger–müller tube detects count rate the geiger müller tube is the most common device used to measure and detect the count rate of radiation each time it absorbs radiation, it transmits an electrical pulse to a counting machine this makes a clicking sound and it displays the count rate on a screen. The activity of a source is defined as the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays measured in decays per second. the unit for activity is the becquerel (bq) where 1 bq = 1 decay per second. Count rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector, such as the geiger muller tube. the illustration below shows how a radioactive sample is decaying over time.
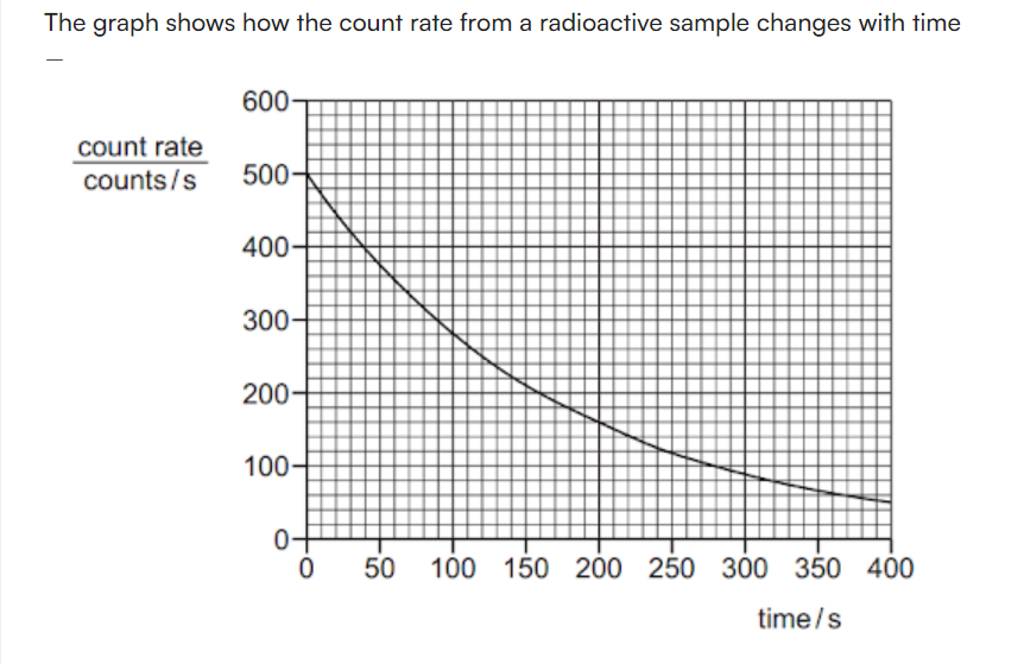
The Graph Shows How The Count Rate From A Radioactive Sample Changes With Not the question you're searching for? a detector measures the count rate from a sample of a radioactive nuclide. the graph shows the variation with time of the count rate. the nuclide has a half life of 20 s. Geiger–müller tube detects count rate the geiger müller tube is the most common device used to measure and detect the count rate of radiation each time it absorbs radiation, it transmits an electrical pulse to a counting machine this makes a clicking sound and it displays the count rate on a screen. The activity of a source is defined as the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays measured in decays per second. the unit for activity is the becquerel (bq) where 1 bq = 1 decay per second. Count rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector, such as the geiger muller tube. the illustration below shows how a radioactive sample is decaying over time.

A Radioactive Sample Is Counted For A Period Of 2 Hr Chegg The activity of a source is defined as the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays measured in decays per second. the unit for activity is the becquerel (bq) where 1 bq = 1 decay per second. Count rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector, such as the geiger muller tube. the illustration below shows how a radioactive sample is decaying over time.
Comments are closed.