8 Vector Raster Data Images Vector And Raster Data Model Vector Vs
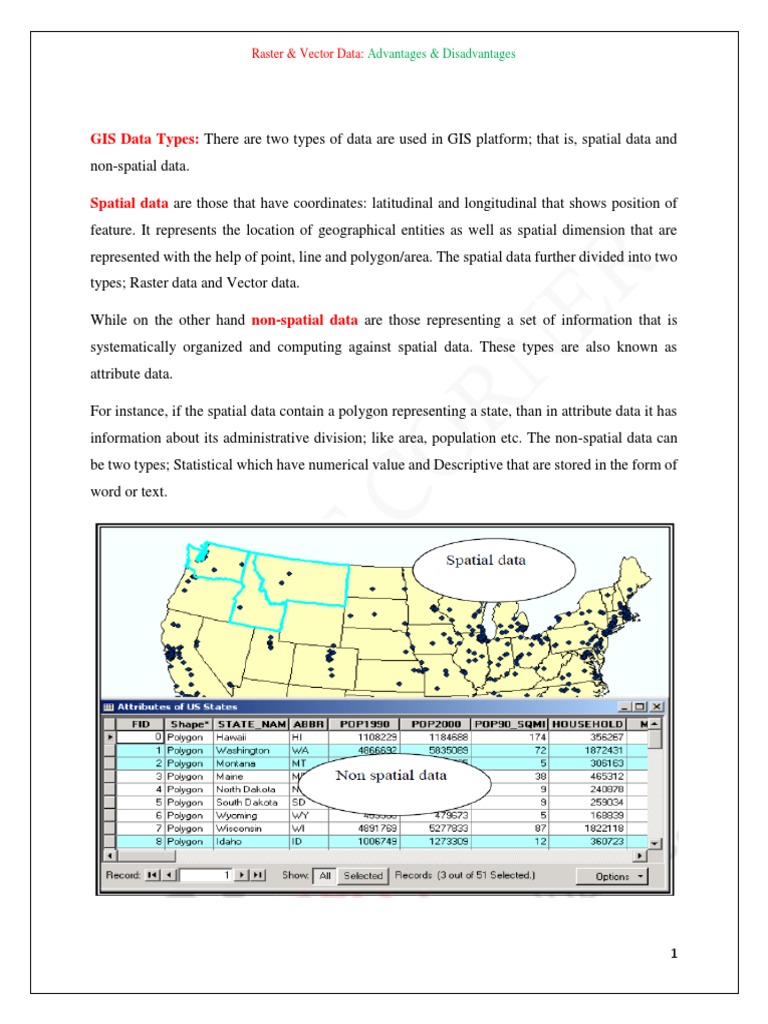
Raster Vector Data Model Pdf The old gis adage “raster is faster, but vector is corrector” comes from the two different fundamental gis models: vector and raster. each of these models has its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications.

Raster Data Model Download Free Pdf Geographic Information System Discover the key differences between vector and raster mapping formats, from data storage and visualization to accuracy and cost considerations in gis applications. Let’s dive into the key differences between raster and vector data, explore their pros and cons, and see how they are used in real world applications — visually explained for better. Two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. in this article, we will discuss the basics of these data models, their differences, and how they are used in gis. Compare raster and vector data models in gis. understand their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases to choose the best for your needs.

Raster Vector Data Representation Pdf Data Model Geographic Two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. in this article, we will discuss the basics of these data models, their differences, and how they are used in gis. Compare raster and vector data models in gis. understand their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases to choose the best for your needs. To determine when to use vector data and when to use raster data, you need to consider the type of geographic features and the requirements for scalability and precision. vector data works better for large coherent areas but not as well for complex shapes. When deciding between raster vs vector models, one of the primary things to consider is whether the data you are representing is continuous or discrete. in general, discrete data is best handled by vector models, while continuous data is best left to raster models. Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for specific climate change applications. before diving into data models, it’s important to distinguish between entities and features. Vector and raster data models are fundamental to geospatial engineering. they represent geographic features in different ways, each with unique strengths. vector models use points, lines, and polygons for precise feature representation, while raster models use grids of cells for continuous phenomena.
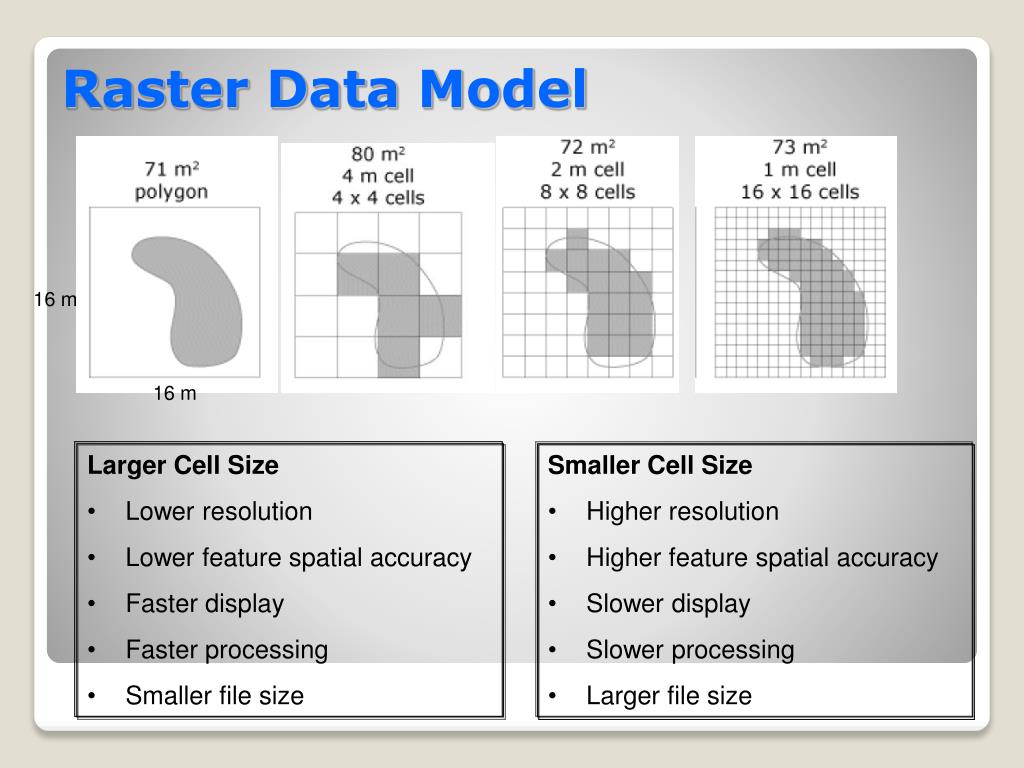
Raster Data Model And Vector Data Model Rilobrooklyn To determine when to use vector data and when to use raster data, you need to consider the type of geographic features and the requirements for scalability and precision. vector data works better for large coherent areas but not as well for complex shapes. When deciding between raster vs vector models, one of the primary things to consider is whether the data you are representing is continuous or discrete. in general, discrete data is best handled by vector models, while continuous data is best left to raster models. Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for specific climate change applications. before diving into data models, it’s important to distinguish between entities and features. Vector and raster data models are fundamental to geospatial engineering. they represent geographic features in different ways, each with unique strengths. vector models use points, lines, and polygons for precise feature representation, while raster models use grids of cells for continuous phenomena.
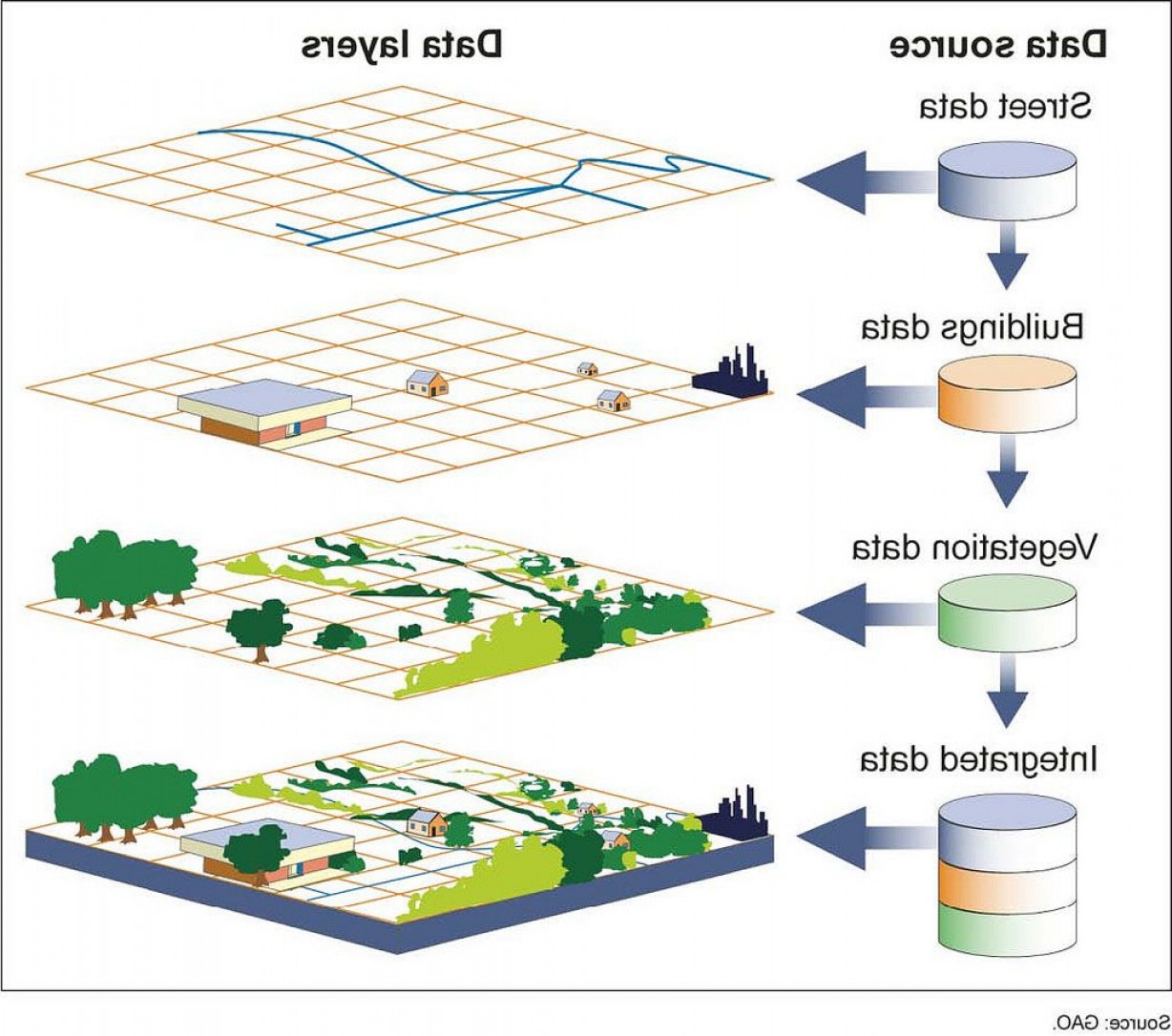
Raster Data Model And Vector Data Model Rilobrooklyn Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for specific climate change applications. before diving into data models, it’s important to distinguish between entities and features. Vector and raster data models are fundamental to geospatial engineering. they represent geographic features in different ways, each with unique strengths. vector models use points, lines, and polygons for precise feature representation, while raster models use grids of cells for continuous phenomena.
Comments are closed.