8 Bit Floating Point Representation With Examples

Solved 8 Bit Floating Point Representation We Will Implement Chegg In the video i show some basic concepts of 8 bit floating point representation with 3 examples. #learnwithacsgrad more. In fixed point notation, there are a fixed number of digits after the decimal point, whereas floating point number allows for a varying number of digits after the decimal point.
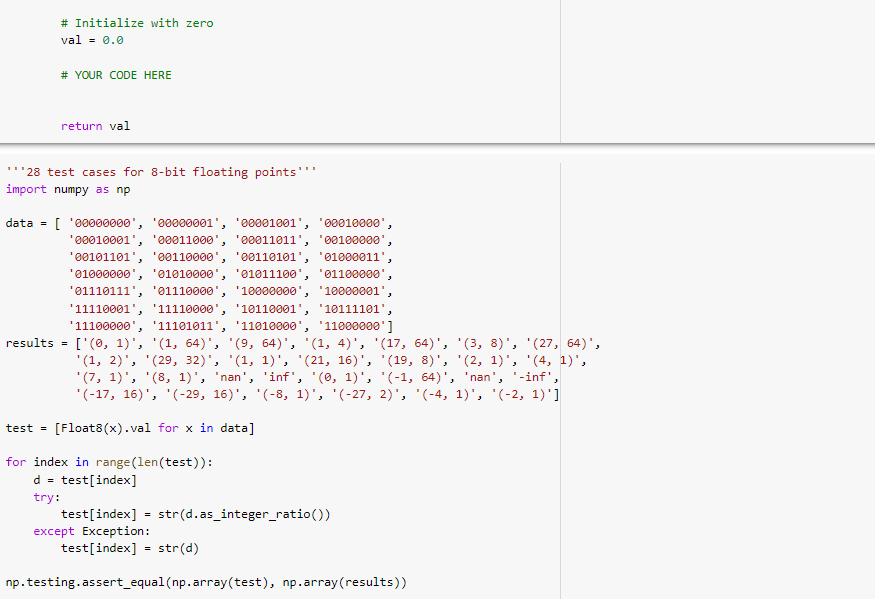
Solved 8 Bit Floating Point Representation We Will Implement Chegg We can represent floating point numbers with three binary fields: a sign bit s, an exponent field e, and a fraction field f. the ieee 754 standard defines several different precisions. — single precision numbers include an 8 bit exponent field and a 23 bit fraction, for a total of 32 bits. In this 8 bit format, one bit is reserved for the sign as usual, three bits are used for the biased exponent, and the remaining four bits are used for the mantissa. This post will look at what an 8 bit floating point number would look like if it followed the pattern of ieee floats or posit numbers. in the notation of the previous post, we’ll look at ieee<8,2> and posit<8,0> numbers. Here are some examples of conversion to and from floating point format. most examples use the 8 bit format described in dr. lowery's textbook. of course, the 8 bit format is useful for instruction, not of much practical value for representing numbers. you will find a few examples using the 32 bit ieee standard format.
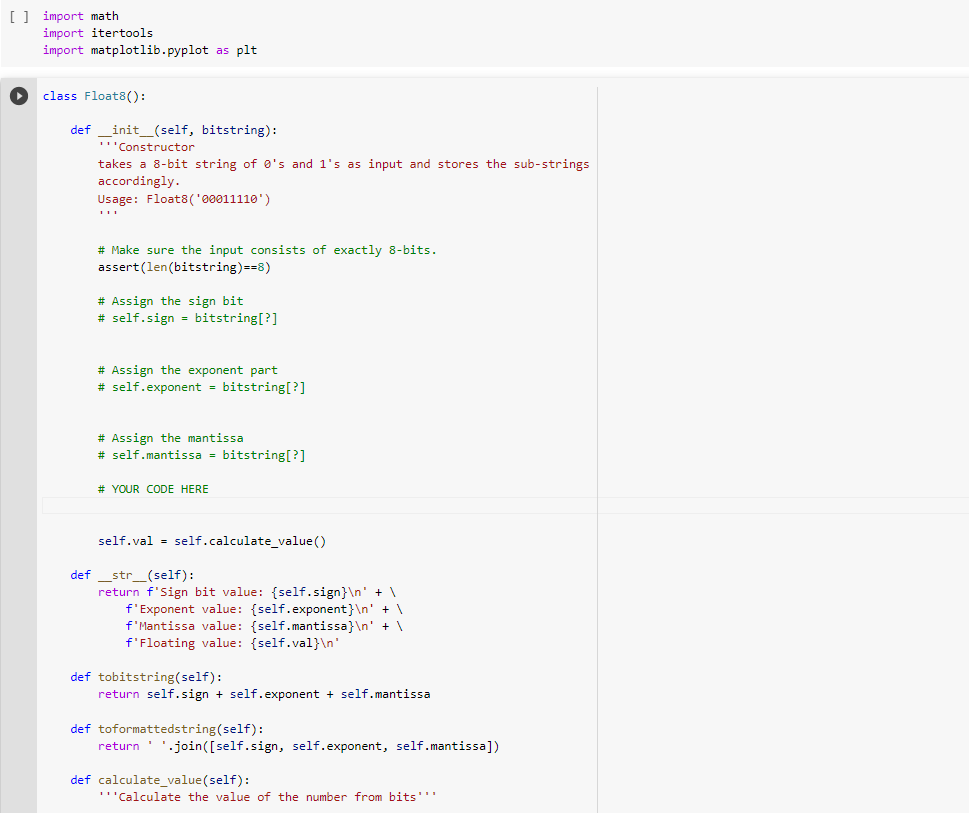
Solved 8 Bit Floating Point Representation We Will Implement Chegg This post will look at what an 8 bit floating point number would look like if it followed the pattern of ieee floats or posit numbers. in the notation of the previous post, we’ll look at ieee<8,2> and posit<8,0> numbers. Here are some examples of conversion to and from floating point format. most examples use the 8 bit format described in dr. lowery's textbook. of course, the 8 bit format is useful for instruction, not of much practical value for representing numbers. you will find a few examples using the 32 bit ieee standard format. Describe and exemplify floating point representation of positive and negative real numbers, using the terms mantissa and exponent. describe the relationship between the number of bits. This guide explores how computers store decimal numbers using floating point representation, why we sometimes get unexpected results like 0.1 0.2 ≠ 0.3, and how modern ai systems use. I'm studying about representing fractional numbers as floating point values. it is going to be an 8 bit representation. somewhere in the text, it is said that: "we use the first bit to represent. This table shows how each of 3 fields of the real floating point representation word is coded with integers [s | exp2pq | frac2pq] in the storage for each ieee 754 standard number type.
Comments are closed.