5 1 Graph Traversals Bfs Dfs Breadth First Search And Depth First Search
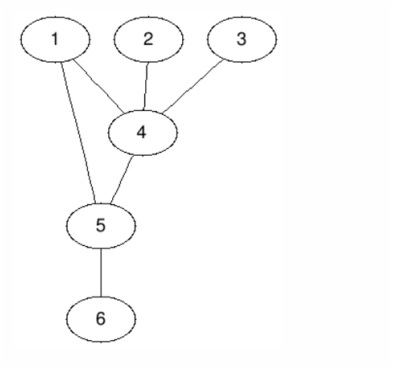
Graph Traversals Dfs Depth First Search And Bfs Breadth First Search There are two common methods for graph traversal: breadth first search (bfs) and depth first search (dfs). bfs explores all the neighboring nodes at the current depth before moving on to nodes at the next depth level, while dfs explores the deepest vertices of a graph before backtracking to explore other vertices. Overview we describe the basic graph traversal algorithms, breadth rst search and depth rst search, and explore their applications.

Solution Breadth First Search Bfs And Depth First Search Graph With bfs, we first examine all nodes at the same level before moving to the next, and ignore the nodes that has been visited. but this time, we consider the gas cost to determine the best route. Two of the most important graph traversal algorithms are breadth first search (bfs) and depth first search (dfs). in this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into these algorithms, exploring their implementations, use cases, and the key differences between them. Many graph applications need to visit the vertices of a graph in some specific order based on the graph’s topology. this is known as a graph traversal and is similar in concept to a tree traversal. In this tutorial, we will focus mainly on bfs and dfs traversals in trees. what is depth first search (dfs)? the algorithm begins at the root node and then it explores each branch before backtracking. it is implemented using stacks. often while writing the code, we use recursion stacks to backtrack.

Solution Breadth First Search Bfs And Depth First Search Graph Many graph applications need to visit the vertices of a graph in some specific order based on the graph’s topology. this is known as a graph traversal and is similar in concept to a tree traversal. In this tutorial, we will focus mainly on bfs and dfs traversals in trees. what is depth first search (dfs)? the algorithm begins at the root node and then it explores each branch before backtracking. it is implemented using stacks. often while writing the code, we use recursion stacks to backtrack. Following are the implementations of simple breadth first traversal from a given source. the implementation uses adjacency list representation of graphs. stl\'s list container is used to store lists of adjacent nodes and a queue of nodes needed for bfs traversal. Breadth first search (bfs) and depth first search (dfs) are two graph traversal methods, with bfs exploring all adjacent vertices systematically using a queue, while dfs uses a stack to explore as deeply as possible along one branch before backtracking. In this article, we will discuss undirected and un weighted graphs. every graph has two components, nodes and edges. let’s see how these two components are implemented in a programming language like java. 1. nodes are implemented by class, structures or as link list nodes.

5 1 Graph Traversals Bfs Dfs Breadth First Search And Depth First Following are the implementations of simple breadth first traversal from a given source. the implementation uses adjacency list representation of graphs. stl\'s list container is used to store lists of adjacent nodes and a queue of nodes needed for bfs traversal. Breadth first search (bfs) and depth first search (dfs) are two graph traversal methods, with bfs exploring all adjacent vertices systematically using a queue, while dfs uses a stack to explore as deeply as possible along one branch before backtracking. In this article, we will discuss undirected and un weighted graphs. every graph has two components, nodes and edges. let’s see how these two components are implemented in a programming language like java. 1. nodes are implemented by class, structures or as link list nodes.
Comments are closed.